

1. Introduction
In April 2016 revelations in the Panama Papers spotlighted the role that banking secrecy – which is offered in so called tax and financial centres and territories – perform in the global economy. The facts have caused increasing concern that banking secrecy lies at the centre of an international web of illegal and criminal conduct. In parallel, several policymakers in advanced countries have emphasised the need for enforcing the blacklisting tool against the territories that breach transparency standards. But does blacklisting work?
Banking secrecy is an evergreen issue in the national and international arenas. In the aftermath of the Global Financial Crisis the fight against bank secrecy as well as against banking secrecy havens has become a political priority in advanced countries.
It is often the case that international organisations as well as national governments do not have strong legal instruments to impose strict measures to prevent and combat banking secrecy. For this reason, soft law practices, such as blacklisting, have been introduced. The aim of the soft law tools is to put the investigated country under intense international financial pressures, using the “name and shame” approach. Under “name and shame approach” institutional regulatory organizations and/or national governments disclose names of non-compliant countries and/or non-compliant banks to the public, supplementing the disclosure with forms of official opprobrium. This approach is increasingly applied in the international context to address policy coordination problems among national policymakers and regulators.
This short paper looks at cross-border capital flows in order to discuss the existence and direction of the so-called stigma effect, i.e. the effect of blacklists in addressing banking secrecy. Country compliance with the international standards of the policy named Anti-Money Laundering and Combating the Financing of Terrorism – AML/CFT hereafter – plays a more and more important role in national policymaking around the world.
Established by the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) in 1999, today the international standard consists of 49 Recommendations, dealing respectively with anti-money laundering (forty recommendations) and combating terrorist financing (nine recommendations). Since 2000, the FATF has periodically issued lists – Blacklists thereafter – of Non-Cooperative Countries and Territories (NCCTs), which identify the jurisdictions that the FATF believes to be non-compliant with international best practices.
In order to prevent and combat illegal financial flows, international organizations do not have hard legal instruments at their disposal; therefore they resort to blacklisting as a soft law practice. The aim of a listing procedure is to put Black-Listed Countries (BLCs) under intense international financial pressure, by employing the “name and shame” approach in order to produce the so-called stigma effect (Masciandaro, 2005a and 2008). By stigma effect we understand an inverse relationship between blacklisting and illegal international capital flows: the event of being blacklisted decreases the international capital flows to a country. Various sources of pressures on a BLC are expected to work.
First, most countries interacting with BLC evaluate their financial transactions to the extent that they are thought to be suspicious. It leads to more stringent and costly monitoring. Banks operating in multiple jurisdictions get more concerned by monetary costs, including compliance costs. The AML/CFT cost of compliance seems to continue to increase, at an average yearly rate of 45 per cent (KPMG 2011).
Furthermore, financial transactions with a BLC can imply reputational costs. Suspicious financial transactions attract more and more attention from supranational organizations, national policymakers and regulators, and international media. For a banking institution, engagement in opaque financial transactions can increase reputational risks. Just to cite the more recent and meaningful episodes, in 2012-15 various international banks were investigated for alleged illicit financial transactions and/or fined, and/or solicited to improve compliance (Powell, 2013). Transactions with BLCs can produce similar negative reputational effects.
Because of the potential damage caused by the stigma effect, international banks may have a strong incentive to avoid business with BLCs.
In the same way, the stigma effect can be considered as a particular result of the “name and shame” approach – i.e. institutional organizations disclose ongoing non-compliance to the public which adds to a disclosure a form of official opprobrium (Brummer, 2012), which is increasingly applied in the international context to address policy coordination problems between national policymakers and regulators (Greene et Boehm, 2012).
But both the existence and the direction of the stigma effect are far from obvious. As was pointed out in pre-vious studies – Masciandaro (2005a and 2008) and Masciandaro et al. (2007) – the AML/CFT non-compliance of a country can be attractive under specific conditions, such as the potential existence of worldwide demand for non-transparent financial transactions. A BLC can be attractive for banking and non-banking institutions seeking to promote lightly regulated products and services to their wealthy and/or sophisticated clients. The inter-national banking industry can have incentives to take advantage from the existence of BLCs. Therefore the stigma effect, meant to be “a stick”, can turn into “a carrot”. The stigma paradox can thus emerge, as a specific case of regulatory arbitrage that creates the so-called “race to the bottom” strategy, which implies the desire to elude more prudent regulation (Barth et al., 2006). This strategy can noticeably influence international capital flows (Houston, 2011).
Finally, we have to consider a third possibility: the behaviour of international banking institutions in the cross-border business can simply be driven by factors other than the stigma effect (Kurdle 2009). In this case, stigma neutrality holds.
In general, the relevance of the stigma effect seems to have become increasingly important in recent times, when policymakers, regulators, and scholars are seeking to understand which institutional and regulatory as well as historical features can attract or discourage international capital flows (Papaioannu, 2009; Reinhardt et al., 2010; Houston et al., 2011; Qureshi et al., 2011; Milesi Feretti and Tille, 2011; Chitu et al., 2013).
The financial effect of regulation can be particularly relevant when the AML/CFT rules are under discussion.
2. Related Literature
Blacklisting procedures were introduced in 2000 and since that time relatively few economic studies on the stigma effect have been produced. The first theoretical and empirical discussion of the stigma effect as a controversial issue was made in Masciandaro (2005a). The study highlighted the fact that in the aftermath of 9/11, growing attention was being paid to the role of lax financial regulation in facilitating money laundering and the financing of terrorism (criminal finance). Two interacting principles are commonly described in the debate on the relationship between money laundering and regulation: a) illegal financial flows are facilitated by lax financial regulation; b) countries adopting lax financial regulation do not co-operate with the inter-national effort aimed at combating criminal finance (International Monetary Fund 1998, Holder, 2003).
These two principles characterize the mandate of the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) for the prevention of money laundering and terrorism finance. On the one hand, to address the problems associated with criminal finance risks, it is fundamental to develop legal standards for regulation. FATF standards (Recommendations) have become the benchmark for measuring the degree of laxity of AML/CFT financial regulation in every single country setting.
On the other hand, faced with the problem of the lack of international harmonization and coordination, in order to monitor the compliance of countries with international standards, the FATF uses a list of specific criteria — consistent with the standards — to determine the BLC jurisdictions, commonly described as blacklists (Alexander, 2001; Masciandaro, 2005a; and Verdugo Yepes, 2011). Blacklisting represents the cornerstone of the inter-national effort to reduce the risk that some countries or territories can turn into havens for criminal financial activities, postulating the stigma effect, i.e. the threat for a listed country to face a drop in capital inflows and then the erosion of its competitive ad-vantage (Hampton and Christensen, 2002).
Here the possibility of the stigma paradox occurs. Focusing on the supply of regulation, it has been stressed (Masciandaro 2005a) that various jurisdictions, notwithstanding the blacklisting threat, delay or fail to change their financial rules, confirming their non-cooperative attitude (reluctant friend effect). Furthermore, notwithstanding the fact that most jurisdictions in the blacklist have enacted regulatory measures in an effort to be removed from it, it remains to be proven that regulatory reform is sufficient to guarantee that a country has really changed its non-cooperative attitude, decreasing its appeal for black capital flows (false friend effect). The existence of the two consequences can nullify the stigma effect, producing stigma neutrality or the stigma paradox.
The theoretical analysis under discussion develops the assumption that lax financial regulation may be a strategic dependent variable for national policy- makers seeking to maximize the net benefits produced by such policy, just as with any other public policy choice. Therefore, given the structural features and endowments of their own country, certain policymakers may find it profitable to adopt financial regulation which accommodates the needs of opaque financial flows – whose existence is given by assumption – and therefore may choose to be a de facto BLC jurisdiction.
The potential incentives to be a BLC have been empirically tested using cross-section estimates, finding that the probability of being a BLC jurisdiction may be linked to specific country features (Masciandaro, 2005a; Verdugo Yepes, 2011; Schwarz, 2011). The rationale for the strategy of being a BLC has been further explored from a theoretical point of view (Unger and Rawlings, 2008; Gnutzmann et al., 2010). Recently, the interactions between the FATF and national governments have been analyzed using a principal-agent framework (Ferwerda, 2012).
The economics of the stigma effect are analyzed in depth in Picard and Pieretti (2011), who focused on the incentives that banks located in a BLC have for complying with the AML/CFT regulation. The blacklisting practice is interpreted as an international pressure policy on the BLC bank and the stigma effect holds when the pressure policy is strong enough. More precisely, the stigma effect becomes effective when the reputational costs linked with the blacklisting procedures – which can harm the bank’s costumers – are higher than the costs for complying with AML/CFT regulation. In the model, international policymakers act efficiently and thus implement optimal blacklisting pressure.
In the real world, non-efficient policymakers are likely to exist; therefore blacklisting pressure can be insufficient and the BLC will continue to attract financial flows, creating the stigma paradox.
The possibility of the stigma paradox has been empirically demonstrated in Rose and Spiegel (2006). Using bilateral and multilateral data from over 200 countries in a gravity framework, the study analyzes the determinants of international capital flows, finding that for a country the status of tax haven and/or money launderer assigned by the international organizations can produce beneficial effects. The analysis confirmed that the desire to circumvent national laws and regulations can be a driver in shifting financial assets abroad.
The search for the impact of blacklisting was also implemented in Kurdle (2008). Using ARIMA techniques on a sample of the blacklisted countries, the study analyzes the financial effects of being listed and delisted.
The results are inconclusive: all three effects – stigma effect, stigma paradox and stigma neutrality – can be found, depending on the time and the observed jurisdiction.
3. Blacklisting and Capital Flows
Recently Masciandaro and Balakina (2016) evaluated empirically the trend, magnitude and robustness of the stigma effect, by focusing on the effect of FATF blacklisting on the relationships between international financial institutions and BLC banking systems. They analysed the relationship between international capital movements and FATF listing/delisting events in 126 countries in the years from 1996 to 2014.
The variable of interest is the dummy variable — FATF — which is equal to 1 if the country is listed in the Financial Action Task Force list of “Non-Cooperative Countries or Territories” and 0 if the country complies with FATF conditions. The FATF variable is constructed using Financial Action Task Force reports “Review to Identify Non-Cooperative countries or Territories: Increasing the Worldwide Effectiveness of Anti-Money Laundering Measures”, published annually in June by the FATF. The report covers the previous 12 months, e.g. the report published in June 2009 represents blacklisting status of the country during 12 month starting from June 2008 till June 2009. We assigned the status “listed” to a country in year , if in June of the country was in the FATF list.
The Financial Task Force List consists of countries perceived to be non-cooperative in the global fight against money laundering and terrorist financing.To evaluate the involvement of a country in terrorist financing and money laundering, the FATF has created a list of recommendations, which includes 40 recommendations on money laundering and nine Special Recommendations on Terrorist Financing. The lack of cooperation of those countries manifests itself as unwillingness or inability to follow FATF recommendations. The international capital flow measure is the growth rate of total foreign claims obtained from the BIS database. Figure 1 represents the average value of International Bank Flows for all 126 countries for the period from 1996 till 2014.
Figure 1. Average value of International Bank Flow, 1996-2014
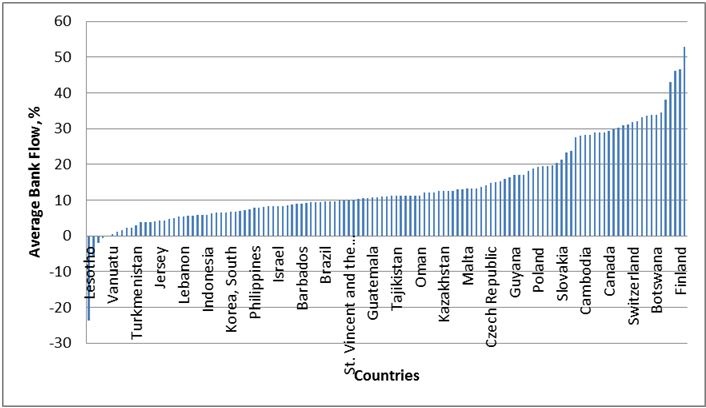
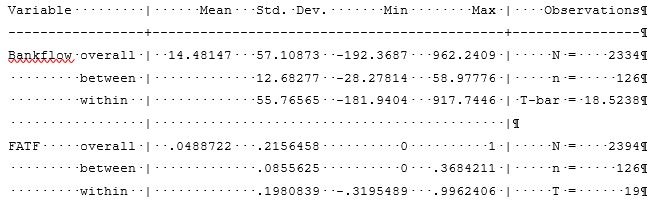
Descriptive statistics for the FATF and Bank Flow variables are represented in Table 1.
Table 1. Descriptive Statistics: Bank Flow and FATF
In total 45 countries were listed during the existence of the FATF List, 10 of these countries are developed, according to World Bank Lists for the time period 1996-2014. The overall econometric analysis – see Masciandaro and Balakina (2016) for further details – shed light on the fact that the FATF variable can be positive and statistically and economically significant. This means that not only does the stigma effect not exist in a systematic way; on the contrary, being listed can be considered in some occasions as a sign of the possibility to get additional profits by escaping taxation.
In other words the empirical analysis tested whether international banking activities respond to the “name and shame” approach, which has been introduced to combat money laundering and terrorism finance. To understand the effects that FATF decisions have on listed countries, the econometric analysis has been focused on how banks react to higher potential costs that can emerge (disappear) when a country is listed (delisted), finding that the stigma effect is weak.
4. Conclusions
Is the era of banking secrecy definitively over, as a G20 official document stated in 2009? Probably not. If it is assumed that banking secrecy is the result of market mechanisms, it is easy to discover that the worldwide demand and supply of banking secrecy are likely to be relevant for a long time to come.
The bottom line is that the growth of criminal and illegal activities systematically generates the demand for banking secrecy, while economic and political incentives can motivate national politicians and international banks to supply banking secrecy. Applying the tools of economics and political economy, it is possible to show that so far international efforts to combat banking secrecy are likely to be ineffective or, even worse, counterproductive. Banking secrecy is unlikely to disappear; it is more realistic to describe it as a dynamic variable with its booms and busts motivated by the changing preferences of both offshore and onshore policymakers. Banking secrecy is a like a tango: it takes two to dance it.
Alexander K. (2001), The International Anti-Money Laundering Regime: The Role of the Financial Action Task Force, Journal of Money Laundering Control, vol.4, n.3, 231-248.
Ardizzi G., Petraglia C., Piacenza M., Schneider F. and Turati G. (2013), Money Laundering as a Financial Sector Crime, CESifo Working Paper Series, n.4127.
Barone R., Masciandaro D. (2011), Organized Crime, Money Laundering and Legal Economy: Theory and Simulations, European Journal of Law and Economics, 2011, vol. 32, n.1, pp. 115-142.
Barth J.R., Caprio J. and R. Levine (2006), Rethinking Bank Regulation: Till Angels Govern, Cambridge, Cambridge University Press.
Brada J.C., Drabek Z. and M.F. Perez (2011), Illicit Money Flows as Motives for FDI, Journal of Comparative Economics.
Brummel C. (2012), Soft Law and the Global Financial System: Rule Making in the 21st Century, Cambridge University Press, New York.
Chitu l., Eichengreen B. and Mehl A.J. (2013), History, Gravity and International Finance, NBER Working Paper Series, National Bureau of Economic Research, n. 18697.
Clark T.S and D.A Linzer (2012), Should I Use Fixed or Random Effects?, Working Paper Series, Department of Political Science, Emory University, March.
Dalla Pellegrina L. and D. Masciandaro (2009), The Risk Based Approach in the New European Anti-Money Laundering Legislation: a Law and Economics View, Review of Law and Economics, Vol.5(2), 290-317.
Dalla Pellegrina L. and D. Masciandaro (2012), Good Bye Light Touch? Macroeconomic Resilience, Banking Regulation and Institutions, Working Paper Series, Paolo Baffi Centre, Bocconi University, Milan.
FATF (2000), Report on Non-Cooperative Countries and Territories, Financial action Task Force, FATF/OECD, Paris.
FATF (2012), International Standard on Combating Money Laundering and the Financing of Terrorism and Proliferation. The FATF Recommendations, Financial Action Task Force, FATF/OECD, Paris.
Ferwerda J. (2012), The International Fight Against Money Laundering, in The Multidisciplinary Economics of Money Laundering, Chapter 7, Dissertation Series, Tjalling C. Koopmans Institute, School of Economics, Utrecht University, Ridderprint, Ridderkerk, 97-118.
FinCEN (2011), Guidance to Financial Institutions Based on the FATF Publication on Anti-Money Laundering and Counter-Terrorist Financing Risks, Financial Crimes Enforcement Network, Department of the Treasury, Washington D.C., July 13.
FitzGerald V. (2004), Global Financial Information, Compliance, Incentives and Terrorist Funding, European Journal of Political Economy, 20, 387-400.
Fraga A. (2004.), Latin America since the 1990s: Rising from the Sickbed?, Journal of Economic Perspectives, 18(2), 89-106.
Franks J., Mercer-Blackman V., Sab R. and R. Benelli (2005), Paraguay. Corruption, Reform and the Financial System, International Monetary Fund, Washington D.C.
Greene E.F. and J.L. Boehm (2012), The Limits of “Name- and- Shame” in the International Financial Regulation, Cornell Law Review, 97(5), 1083-1140.
Gnutzmann H., K.J. Mc Carthy, B. Unger (2010), Dancing with the Devil: Country Size and the Incentive to Tolerate Money Laundering, International Review of Law and Economics, 30, 244-252.
Holder, W.E (2003), The International Monetary Fund’s Involvement in Combating Money Laundering and the Financing of Terrorism, Journal of Money Laundering Control, vol.6, n.4, 383-387.
Hampton M.P and J. Christensen (2002), Offshore Pariahs? Small Island Economies, Tax Havens, and the Reconfiguration of Global Finance, World Development, 30(6), 1657-1673.
Houston J.F., Lin C. and Y. Ma (2011), Regulatory Arbitrage and International Bank Flows, Journal of Finance, forthcomings.
IMF (1998), Money Laundering. The Importance of International Countermeasures, address by Michel Camdessus, Plenary Meeting of the FATF, International Monetary Fund, Washington D.C., pp. 1-4.
IMF (2009), Paraguay: Detailed Assessment Report on Anti-Money Laundering and Combating the Financing of Terrorism, IMF Country Report Series, International Monetary Fund, Washington D.C., n. 235.
IMF (2011), Paraguay: Financial System Stability Assessment-Update, IMF Country Report Series, International Monetary Fund, Washington D.C., n. 235.
Kaufmann D., Kraay A. and M. Mastrucci, (2008), Governance Matters VII: Aggregate and Individual Governance Indicators, 1996-2007, Policy Research Working Paper Series, World Bank, Washington, DC, n. 4654.
KPMG, (2011), Global Anti – Money Laundering Survey, at kpmg.com.
Kudrle R., (2009), Did Blacklisting Hurt the Tax Havens?, Journal of Money Laundering Control, Vol. 12 (1), 33-49.
Lane P. and G.M. Milesi Ferretti (2003), International Financial Integration, IMF Staff Papers, International Monetary Fund, 50, 82-113.
Masciandaro D. (2005a), False and Reluctant Friends? National Money Laundering Regulation, International Compliance and Non-Cooperative Countries, European Journal of Law and Economics, 2005, n.20, 17-30.
Masciandaro D. (2005b), Financial Supervision Unification and Financial Intelligence Units: A Trade Off? Journal of Money Laundering Control, Vol. 8(3), 354-370.
Masciandaro D. (2008), Offshore Financial Centres: the Political Economy of Regulation, European Journal of Law and Economics, Vol. 26, 307-340.
Masciandaro D., Balakina O. and D’Andrea A. (2016), Bank Secrecy in Offshore Centres and Capital Flows: Does Blacklisting Matter?, Baffi Carefin Working Paper Series, (forthcoming).
Masciandaro D., Takats E. and Unger B. (2007), Black Finance. The Economics of Money Laundering, Edward Elgar, Cheltenham.
Masciandaro D., Pansini R.V. and M. Quintyn (2013), The Economic Crisis: Did Supervisory Architecture and Governance Matter, Journal of Financial Stability.
Milesi Ferretti G.M and Tille C. (2011), The Great Retrenchment: International Capital Flow During the Global Financial Crisis, Working Paper Series, Hong Kong Institute for Monetary Research, n.38.
Papaioannou E. (2009), What Drives International Financial Flows? Politics, Institutions and Other Determinants, Journal of Development Economics, 88, 269-281.
Picard P.M and P. Pieretti (2011), Bank Secrecy, Illicit Money and Offshore Financial Centres, Journal of Public Economics, 95 (7-8), 942-955.
Powell J.H. (2013), Anti-Money Laundering and the Banking Secrecy Act, Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, Committee on Banking, Housing and Urban Affairs, U.S. Senate, Washington D.C., March 7, mimeo.
Qureshi M.S., Ostry J.D., Ghosh A.R. and M. Chamon (2011), Managing Capital Inflows: The Role of Capital Controls and Prudential Policies, NBER Working Paper Series, n.17363.
Ramon – Ballester F. and T. Wezel (2007), International Financial Linkages of Latin American Banks. The Effects of Political Risks and Deposit Dollarization, ECB Working Paper Series, European Central Bank, n.744.
Reinhardt D., Ricci L.A. and T. Tressel (2010), International Capital Flows and Development: Financial Openness Matters, IMF Working Paper Series, International Monetary Fund, n.235.
Roodman (2006), How to Do Xtabond2: An Introduction to Difference and System GMM in Stata, Working Paper Series, Center for Global Development, n.13.
Rose A.K. and M. Spiegel (2006), Offshore Financial Centers: Parasites or Symbionts?, Economic Journal, 117(523), 1310-1335.
Schwarz P. (2011), Money Launderers and Tax Havens: Two Sides of the Same Coin?, International Review of Law and Economics, 31, 37 – 47.
Taka tz E. (2011), A Theory of “Crying Wolf”: The Economics of Money Laundering Enforcement, Journal of Law, Economics and Organization, 27(1), 32-78.
Unger B. and Rawlings G. (2008), Competing for Criminal Money, Global Business and Economics Review, 10(3), 331-352.
Verdugo Yepes C. (2011), Compliance with the AML/CFT International Standard: Lessons from a Cross-Country Analysis, IMF Working Paper Series, International Monetary Fund, n.177.
World Bank (2008), Bank Regulation and Supervision Survey, World Bank Group, Washington D.C.
The author thanks Morten Balling, Ernest Gnan and David T. Llewellyn for their useful insights on earlier drafts. The usual disclaimer applies.