

Executive Summary
The 2024 Digitalization Survey by the Bank of Albania provides an in-depth analysis of the Albanian banking sector’s digital transformation, capturing the progress, challenges, and opportunities in its journey toward a digital-first economy. Digital transformation is reshaping the sector, driven by the need to meet evolving customer demands, enhance operational efficiencies, and align with international regulatory standards. This survey reveals that 93% of banks in Albania have established dedicated digital transformation departments, reflecting a strategic commitment to innovation. Widely adopted technologies such as mobile banking, APIs, and e-banking platforms have redefined service delivery, while plans for integrating artificial intelligence, blockchain, and digital wallets highlight a forward-looking approach.
Despite notable progress, the sector faces persistent challenges. Limited digital literacy among the population, coupled with low trust in digital financial services, hampers adoption. High implementation costs and cybersecurity risks further complicate the digitalization process, while regulatory gaps and reliance on third-party providers create additional barriers. Cybersecurity remains a critical concern, with banks reporting increased exposure to cyber threats. While 65% of banks consider themselves well-prepared, the evolving nature of cyber risks underscores the need for constant vigilance.
The Bank of Albania plays a pivotal role in supporting this transition. Initiatives such as the establishment of a regulatory sandbox offer a controlled environment for FinTech innovation, fostering collaboration between banks, technology firms, and regulators. The alignment of Albania’s regulatory framework with EU directives, including the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA), is another key priority, aimed at ensuring seamless integration with the broader European financial ecosystem. Moreover, the Bank emphasizes strengthening consumer protection and enhancing digital literacy to build trust in digital financial services.
This report concludes that while the Albanian banking sector has made significant strides in payments and customer service, challenges such as digital literacy gaps and cybersecurity risks must be addressed to unlock its full potential. By prioritizing collaboration, regulatory alignment, and education, the sector is well-positioned to lead Albania’s transition to a resilient and inclusive digital economy. The findings and recommendations of this survey serve as a roadmap for the sector’s continued transformation, fostering growth, innovation, and competitiveness in a rapidly evolving financial landscape.
Digital transformation is rapidly reshaping the banking industry worldwide, and the Albanian banking sector is no exception. This shift involves more than just adopting new technologies—it represents a fundamental change in how banks operate, interact with customers, and deliver services. By integrating innovative digital tools and strategies, known collectively as FinTech1, banks can meet evolving customer demands, stay competitive, and ensure secure, accessible, and efficient financial services. The evolution of digital banking is not merely a response to technological advancements but a strategic imperative that reflects the broader societal shift towards digitalization. In this context, Albania finds itself at a pivotal juncture, navigating the complexities and opportunities of digital transformation within its financial sector.
The concept of digital transformation in banking encompasses the modernization of processes, products, and services through the adoption of digital technologies. This transformation spans from online and mobile banking platforms to advanced digital payment systems and data-driven decision-making tools. As customer expectations evolve, driven by the millennial generation’s preference for convenient, digital-first services, banks globally—and in Albania—are prioritizing digitalization to remain relevant. In Albania, the demand for banking digitization is further reinforced by the societal shift to a digital-first era, where access to technology influences consumer behavior and market dynamics.
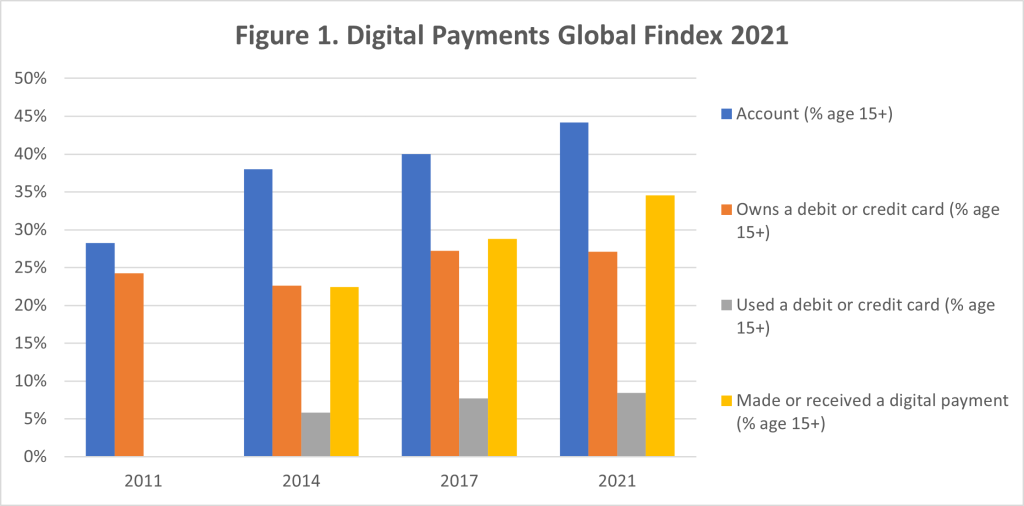
In Albania, the trend of digital adoption is steadily rising. According to the Global Findex report2, 83.1% of the population3 had internet access in 2022, compared to 76% in 2021. This significant increase demonstrates the public’s readiness to engage with digital services. Yet, while internet usage for leisure and information purposes is widespread, fewer Albanians utilize online platforms for business transactions, online purchases, or digital payments. The gap between digital access and digital financial service usage underscores a persistent challenge in digital literacy and trust. For instance, as highlighted in the Digital Payments Global Findex 2021 chart, the percentage of adults in Albania making and receiving digital payments has grown over time. However, a substantial segment of the population still holds accounts without engaging in digital transactions, reflecting barriers such as limited financial literacy and concerns over digital security.
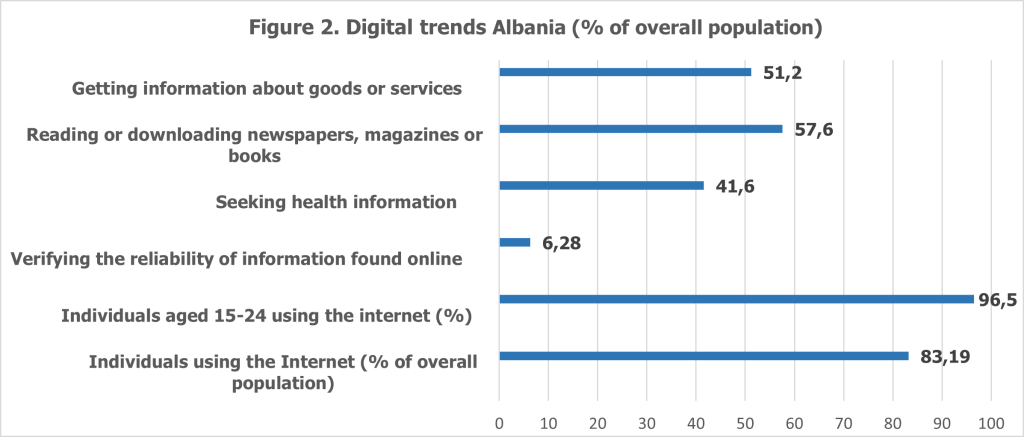
Furthermore, broader digital trends reveal a nuanced picture of Albania’s digital readiness. While activities like reading online newspapers (57.6%) and obtaining goods and services information (51.2%) are common, only 6.28% of the population actively verifies the reliability of online information. This low level of digital information verification indicates a gap in critical digital skills, which poses challenges not only for the adoption of digital banking solutions but also for fostering a culture of digital trust and competency. Addressing this gap requires a comprehensive approach to education and awareness-building, particularly in areas such as online financial transactions and cybersecurity.
The Albanian banking sector, supervised by the Bank of Albania, is actively engaging in initiatives to promote safe, inclusive, and sustainable digital financial services. These efforts align with global best practices, where digital transformation is viewed as both an operational upgrade and a strategic response to the evolving economic landscape. The Bank of Albania’s commitment to advancing financial inclusion through digital means is evident in its policy measures and public awareness campaigns. By fostering trust in digital systems and enhancing digital literacy, the institution aims to bridge the gap between digital access and utilization.
Private banks in Albania are also playing a crucial role in this digital transition. By introducing mobile banking apps, online payment gateways, and other digital tools, these institutions are reshaping customer experiences and operational efficiencies. These advancements reflect a broader shift towards a digital-first approach, where technology serves as a catalyst for innovation and growth within the financial sector. However, the full potential of these developments can only be realized through the concerted efforts of stakeholders, including policymakers, financial institutions, and the public.
Despite these advancements, significant challenges remain. A large portion of the Albanian population remains underbanked or unbanked, with limited access to digital financial services. Furthermore, the gap in ICT literacy—as evidenced by low competency levels in online financial transactions—poses a critical hurdle to widespread adoption. Addressing these barriers requires targeted interventions, such as education programs focused on digital skills, initiatives to build trust in digital systems, and the development of user-friendly platforms tailored to the needs of diverse demographic groups.
Recognizing the importance of understanding current trends and challenges in the digitalization journey, the Bank of Albania conducted its annual FinTech Survey in September 2024. This survey aimed to gather insights into the current state of digital transformation within Albania’s banking sector, focusing on the drivers behind digital initiatives, technological adoption, and preparedness to manage associated risks. This report seeks to present and analyze the findings of this survey, providing a comprehensive understanding of the progress and challenges in Albania’s digital banking landscape.
The structure of the report begins with an overview of the methodology used in conducting the survey, followed by a detailed analysis of the results. It then delves into the implications of the findings for the banking sector and concludes with actionable recommendations for advancing digital transformation in Albania’s financial ecosystem. By bridging the gap between data and strategy, this report aims to contribute to the ongoing dialogue on digitalization in the Albanian banking sector, highlighting its potential to foster growth, inclusivity, and resilience.
The 2024 Digitalization Survey undertaken by the Bank of Albania underscores a commitment to advancing the country’s financial sector in alignment with global trends. The objective of this survey was to provide a thorough analysis of digital transformation within Albania’s banking sector, capturing both the progress made and the challenges encountered. By identifying the drivers of digital initiatives, the adoption of emerging technologies, and the sector’s capacity to manage associated risks, the survey sheds light on the state of digitalization in Albania’s financial ecosystem.
At its core, the survey aims to understand the strategic motivations propelling banks toward digital transformation. It investigates the alignment of digital initiatives with customer expectations, operational efficiencies, and the overarching goal of financial inclusion. Digital transformation is no longer a mere operational enhancement; it has become an essential factor in maintaining competitiveness, particularly as financial technologies redefine customer interactions and market landscapes. The findings aim to offer insights that enable financial institutions to better align their strategies with the evolving demands of a digital-first economy.
The scope of the 2024 Digitalization Survey was designed to be inclusive and representative of the Albanian banking sector as a whole. Responses were collected from all active banks operating in the Albanian market as of August 31, 2024. The data collection process encompassed a diverse range of digitalization aspects, from the integration of new technologies to the implementation of risk management frameworks. This comprehensive approach ensures that the survey results accurately reflect the current state of digital transformation across the sector.
To gain a holistic understanding, the survey probed three critical dimensions of digitalization. First, it explored the primary drivers of digital transformation, examining the motivations behind the adoption of FinTech solutions. These include factors such as customer demand for convenience, the need to streamline operations, and the strategic imperative to remain competitive in a rapidly digitizing world. Second, the survey delved into the adoption of innovative technologies within the banking sector, such as mobile banking applications, artificial intelligence-powered customer service tools, and advanced digital payment systems. Finally, it assessed the preparedness of banks to address the risks associated with digital transformation, including cybersecurity threats, data privacy concerns, and operational vulnerabilities.
In terms of methodology, the survey employed a mixed-methods approach, combining structured questionnaires with qualitative interviews. This approach allowed for the collection of both quantitative data and nuanced insights from key stakeholders. By integrating diverse perspectives, the survey ensures a comprehensive understanding of digital transformation in the Albanian banking sector. Furthermore, the scope of the survey reflects a forward-looking perspective, emphasizing not only the current state of digitalization but also the strategic priorities that will shape the sector’s future.
Through its objectives and scope, the 2024 Digitalization Survey seeks to bridge the gap between existing capabilities and emerging opportunities within the banking sector. By aligning these findings with the broader vision of financial inclusion and technological advancement, the Bank of Albania aims to pave the way for a more resilient and inclusive financial system. Ultimately, this survey serves as a critical tool for guiding Albania’s digital transformation journey, ensuring that the country’s banking sector remains at the forefront of innovation and growth in an increasingly digital world.
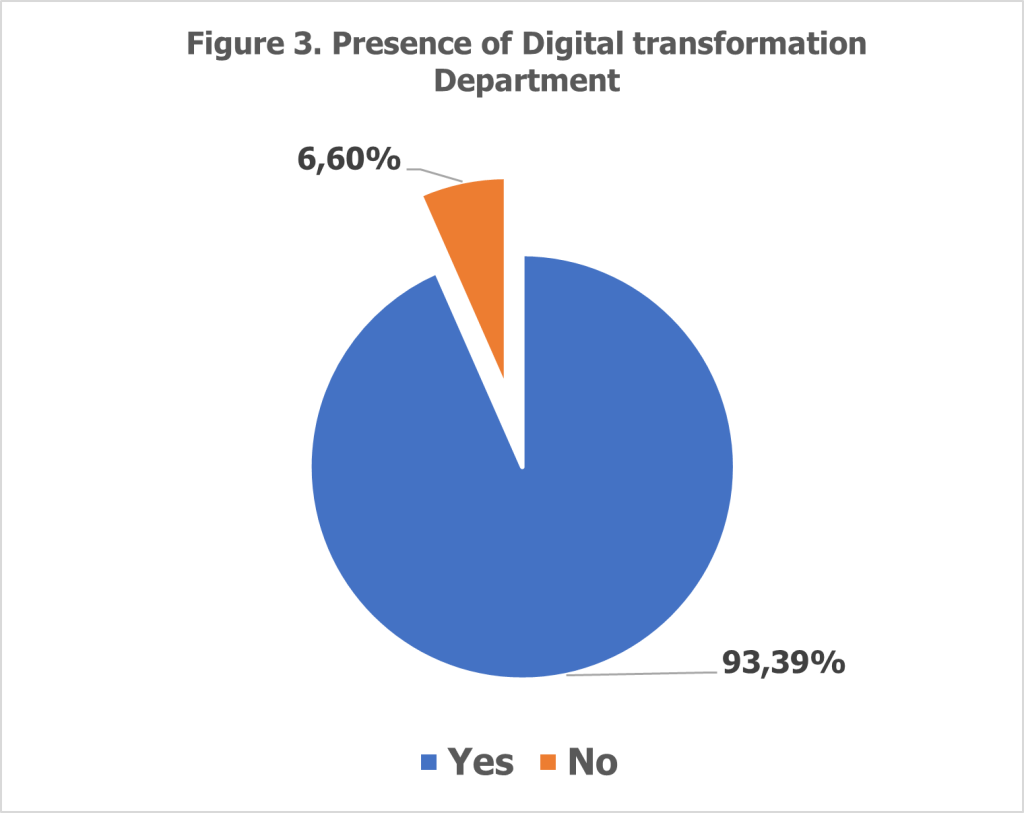
The findings of the 2024 Digitalization Survey reveal that the majority of banks in Albania have made significant strides in their digital transformation journeys. Notably, 10 banks, collectively representing 93.39% of the total assets in the banking sector, have established dedicated digital transformation departments or specialized teams tasked with implementing and managing FinTech initiatives. These departments serve as the cornerstone for driving innovation, facilitating the adoption of new technologies, and ensuring that digital banking services align with evolving customer expectations.
In contrast, only one bank, accounting for 6.60% of the sector’s assets, reported the absence of a digital transformation function. As illustrated in Figure 3, this underscores the sector-wide recognition of the importance of digital transformation as a strategic priority. The establishment of dedicated departments reflects a proactive approach by Albanian banks to allocate resources, expertise, and leadership toward fostering technological advancements within their operations.
The widespread adoption of digital transformation initiatives signals a broader commitment to embracing change within the Albanian banking sector. By focusing on the integration of cutting-edge financial technologies, banks are better positioned to address the growing demand for seamless and efficient digital services. These efforts not only enhance customer experiences but also improve operational efficiencies, enabling banks to remain competitive in an increasingly digitalized financial landscape.
Furthermore, the establishment of digital transformation departments has enabled banks to accelerate the implementation of key initiatives, such as the deployment of mobile banking platforms, the introduction of AI-powered customer service tools, and the expansion of digital payment systems. These advancements contribute to creating a robust and innovative financial ecosystem, supporting Albania’s transition to a digital-first economy. However, the survey also highlights the challenges faced by some institutions in adopting such initiatives, particularly in terms of resource constraints and the need for capacity building.
Overall, the results of the 2024 survey provide a comprehensive overview of the state of digitalization within Albania’s banking sector. The findings emphasize the critical role of institutional commitment and strategic resource allocation in driving digital transformation. By leveraging these insights, the Bank of Albania and other stakeholders can identify opportunities to support the sector’s ongoing transition, ensuring that all institutions—regardless of size or market share—can benefit from the advantages of digital banking.
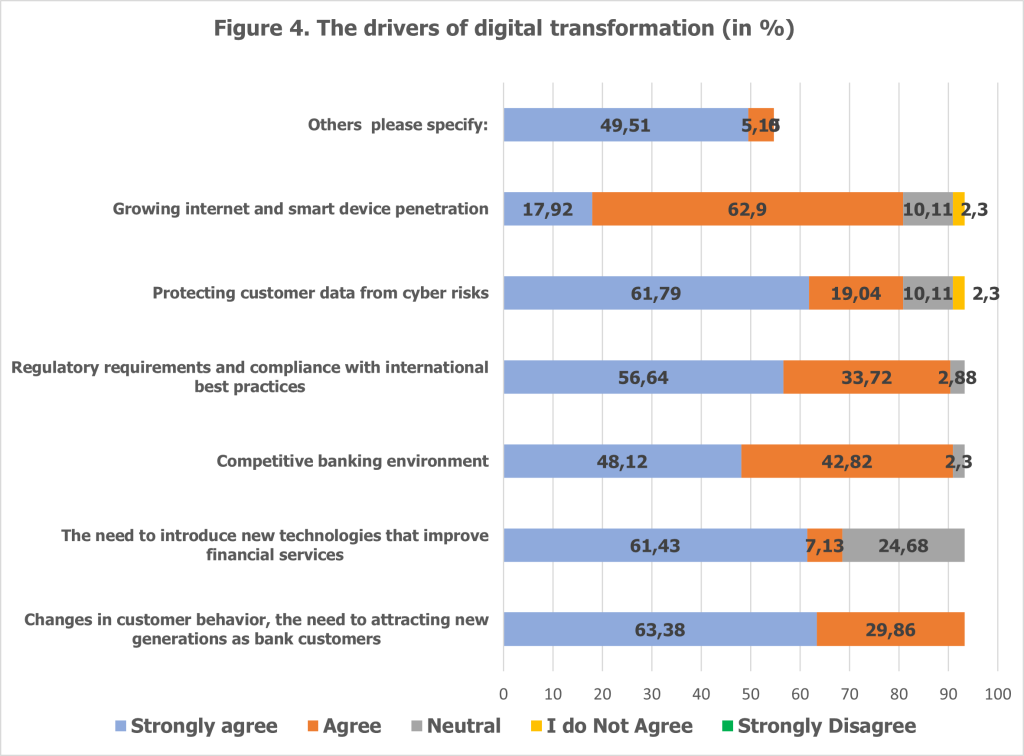
The survey results reveal several key drivers behind the Albanian banking sector’s adoption of FinTech solutions, underscoring the strategic motivations for embracing technological innovation. The survey identified several key drivers for FinTech investments in Albania’s banking sector4 (see Figure 4).
Among these drivers, changes in customer behavior emerged as a primary factor. Seven banks, representing 63.4% of total assets, strongly agreed that the shift in customer preferences, particularly the need to attract new generations, was a major reason for investing in FinTech. The growing demand for personalized, convenient, and accessible banking experiences across digital platforms has driven banks to prioritize customer-centric innovations to maintain competitiveness and reduce the risk of customer attrition.
Technological advancements also play a critical role in shaping FinTech adoption. Eight banks, accounting for 61.43% of total assets, highlighted the necessity of incorporating new technologies to improve financial services. This includes initiatives such as enhancing mobile banking functionalities, deploying AI-based solutions for customer service, and optimizing internal operations through automation. The rapid evolution of financial technologies has created opportunities for banks to redefine service delivery and operational efficiency.
Cybersecurity concerns are another significant driver, with six banks, representing 61.79% of assets, strongly agreeing on the importance of safeguarding customer data from cyber risks. Given the sensitive nature of financial information, robust cybersecurity measures are essential for maintaining customer trust and ensuring the security of digital platforms. These concerns have led to increased investments in advanced security protocols and infrastructure.
Regulatory compliance and alignment with international best practices were cited by five banks (56.6% of assets) as a major motivator for FinTech adoption. The dynamic regulatory environment necessitates ongoing adjustments to meet global standards, and digital transformation provides banks with the tools to achieve compliance efficiently. An additional four banks, accounting for 33.7% of assets, agreed that regulatory requirements reinforce the need for technological innovation within the sector.
Finally, the competitive banking environment has encouraged FinTech adoption, with five banks (48.14% of assets) strongly agreeing and four others (42.8% of assets) agreeing that technological innovation is key to sustaining competitive advantages. In a rapidly evolving market, digital transformation enables banks to differentiate their services, improve customer engagement, and enhance operational agility.
Beyond these primary drivers, several banks also identified internal process automation, enhanced customer experience, and operational optimization as critical factors for adopting FinTech solutions. For instance, institutions such as Raiffeisen Bank and Union Bank emphasized the importance of automation for efficiency gains, while others highlighted improvements in customer satisfaction and the ability to scale operations effectively.
While digital transformation promises numerous benefits, the journey is fraught with significant obstacles. The findings of the 2024 Digitalization Survey reveal several challenges that banks in Albania face as they adopt FinTech solutions and innovate their service offerings (see Figure 5).
A notable challenge is the low digital customer activity, primarily attributed to the high preference for cash transactions among the population. Nine banks, representing 68.19% of the sector’s total assets, agreed or strongly agreed that limited digital engagement among customers impedes digital transformation. This challenge aligns with the Global Findex 2021 report, which showed that while Albanians are active internet users for leisure and news, fewer engage with online platforms for financial transactions. Addressing this issue requires targeted public awareness campaigns and incentives to encourage the use of digital banking services.
Another significant obstacle is the low technological skills of the population. Seven banks, holding 43.19% of total assets, identified this as a barrier to digitalization. The reliance on traditional banking customers rather than a digitally adept generation highlights the urgent need for public digital literacy initiatives. Equipping the population with basic technological skills will play a critical role in supporting Albania’s transition to a digital-first economy.
Internally, banks face challenges in building expertise for FinTech projects. While 65.7% of banks disagreed with the notion that they lack expertise, 30.95% acknowledged limited internal capacity as a hindrance. This underscores the importance of upskilling employees through specialized training and professional development programs to meet the demands of digital transformation.
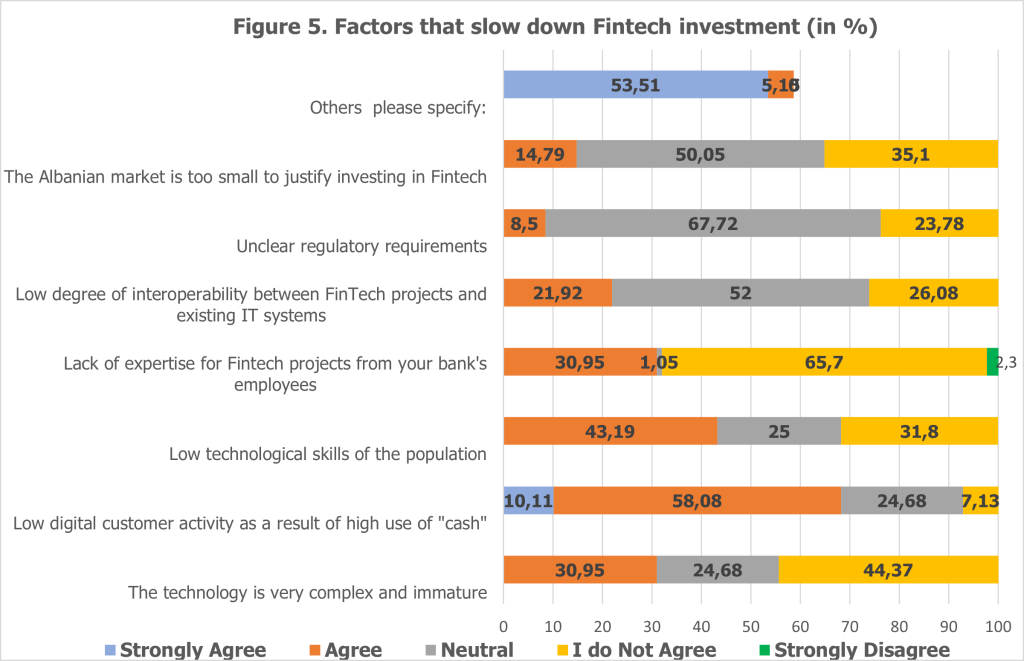
High investment costs and cybersecurity risks also present ongoing challenges. Two banks, representing 28.8% of the sector’s assets, strongly agreed that these factors impede digitalization. The financial demands of implementing new infrastructure, combined with the need for robust security measures to protect customer data, remain significant hurdles. Overcoming these challenges will require innovative financing models and partnerships to share resources and expertise.
Regulatory barriers further complicate digital transformation efforts. Concerns around unclear regulatory requirements and obstacles related to third-party providers for distance identification and electronic signatures were cited by several banks. Close collaboration with regulatory authorities is essential to streamline compliance processes and foster an environment conducive to digital innovation.
Lastly, the competitive disadvantages of traditional banks compared to agile FinTech startups pose another challenge. One bank highlighted that FinTech firms’ ability to innovate swiftly gives them a distinct advantage in the market. To remain competitive, traditional banks must adopt a more flexible approach to innovation and form strategic partnerships with FinTech companies.
Additional challenges noted by banks include the small size of the Albanian market, low interoperability between FinTech projects and existing IT systems, and the complexity of immature technologies. These factors further underscore the multifaceted nature of the digital transformation journey and the need for a coordinated effort among stakeholders to overcome these barriers.
The survey reveals that Albanian banks have embraced a variety of digital technologies as part of their transformation journey (see Figure 6).
These technologies represent a concerted effort by financial institutions to modernize operations, enhance customer experiences, and compete in a rapidly evolving digital landscape. Among the key technologies implemented by Albanian banks, mobile banking stands out as the most universally adopted solution. All banks have integrated mobile banking into their service portfolios, providing customers with the ability to perform essential tasks such as checking balances, transferring funds, and viewing transaction histories directly from their smartphones. This technology has revolutionized the banking experience in Albania, offering 24/7 access and unparalleled convenience, making financial services more accessible and efficient for customers.
Another widely adopted technology is the use of Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), which have been implemented by 83.8% of banks. APIs facilitate seamless data sharing and integration across various platforms, enabling enhanced customer experiences and supporting interactions with third-party applications such as payment processors and financial management tools. By leveraging APIs, banks have positioned themselves to connect with new markets and drive innovation, allowing developers to build custom integrations that address specific customer needs and market demands.
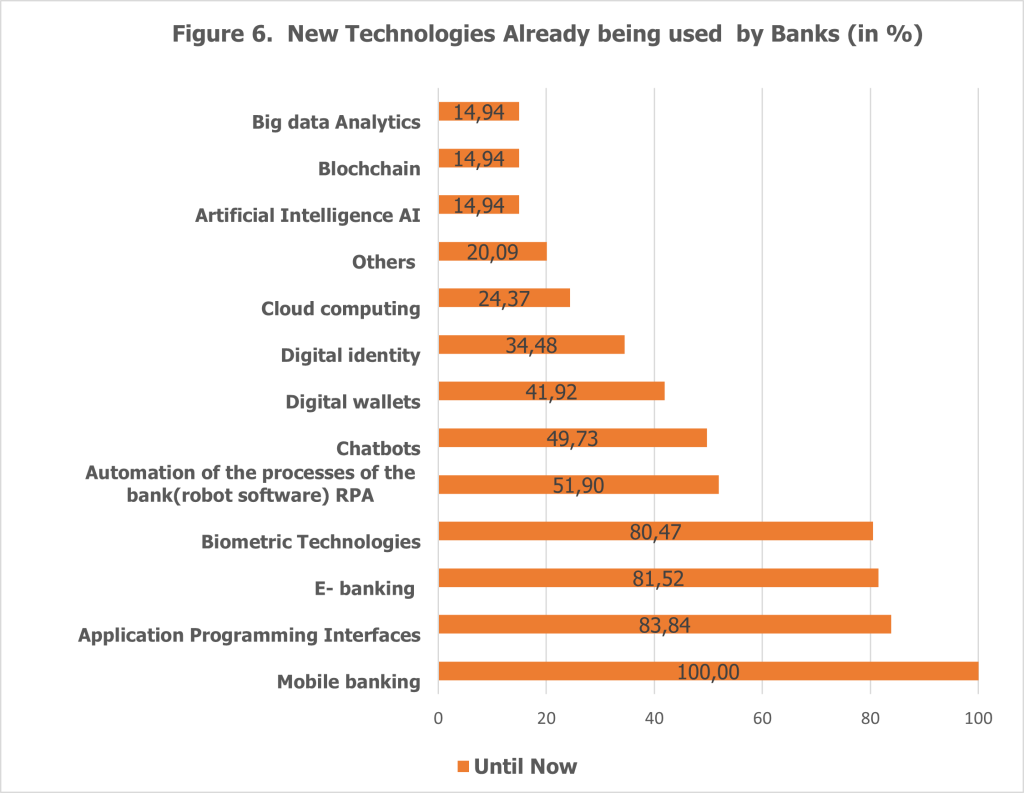
E-banking platforms, adopted by 81.5% of banks, have further enhanced the accessibility of financial services in Albania. These platforms enable customers to perform a wide range of banking activities online, from managing accounts to paying bills and transferring funds. The introduction of e-banking has reduced the reliance on physical bank visits, streamlining operations and significantly improving customer satisfaction. This technology has become a cornerstone of modern banking, empowering customers with the flexibility and convenience of digital interactions.
Biometric technologies have also gained traction, with 80.47% of banks utilizing these solutions to enhance security and identity verification. By employing biometric systems such as fingerprint recognition, facial scans, and other biometric data, banks have strengthened the security of digital transactions. This technology not only reduces the risk of fraud and unauthorized access but also builds customer trust by offering a robust layer of protection for sensitive financial information.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has been adopted by 51.9% of banks to streamline back-office operations and automate repetitive tasks. This technology represents an evolution of workflow management systems, enabling banks to improve operational efficiency, reduce manual errors, and allocate resources to more strategic initiatives. RPA has proven to be a valuable tool for optimizing internal processes and supporting the scalability of banking operations.
Digital identity solutions, currently used by 41.9% of banks, have become an essential component of online banking and digital transactions. These solutions facilitate secure, remote identity verification, simplifying the customer onboarding process and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. By enhancing security and convenience, digital identity technologies support the expansion of digital banking services and contribute to improved customer experiences.
While widely adopted technologies like mobile banking and APIs have paved the way for digital transformation, emerging solutions such as blockchain and big data analytics are still in their infancy. Only 14% of banks have implemented these technologies, reflecting a cautious approach to innovation. Banks appear to prioritize more established solutions as they navigate the complexities of resource allocation and market readiness. This gradual adoption strategy highlights the need for Albanian banks to balance the pursuit of cutting-edge innovation with the practicalities of their operational and customer environments.
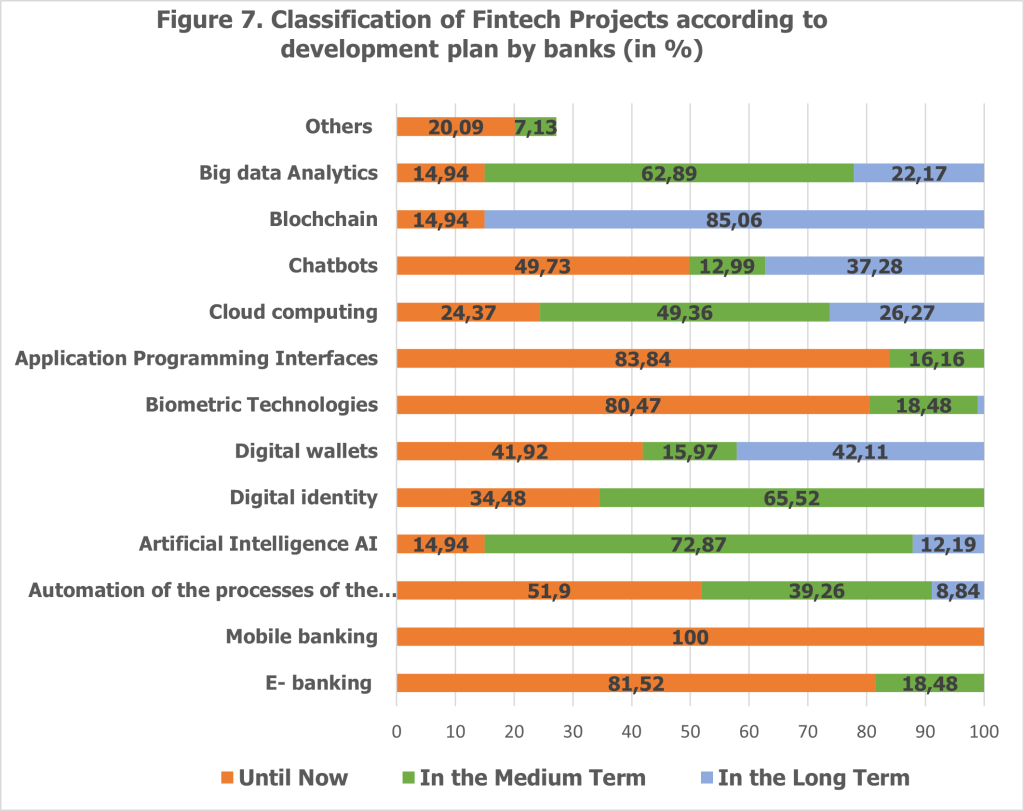
Looking forward, Albanian banks are set to expand their technological capabilities with several key FinTech projects planned for the medium and long term (see Figure 7).
Digital identity technology, already in use, is expected to see further development in 65.5% of banks over the medium term. This expansion underscores the increasing importance of secure, remote identity verification in facilitating digital banking and e-commerce transactions.
Digital wallets, although currently in the early stages of adoption, are projected for long-term implementation by 42.11% of banks. This highlights a growing interest in mobile-based payment solutions that cater to the needs of tech-savvy customers and support the shift towards a cashless economy.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is another major focus area, with 72.8% of banks planning medium-term adoption and an additional 12.2% targeting long-term implementation. AI is poised to transform banking operations by enhancing analytics, customer service, and fraud detection capabilities. Its integration will enable banks to deliver more personalized and efficient services while optimizing risk management processes.
Cloud computing, already utilized by 24% of banks, is set for further development in 49.36% of institutions over the medium term. The scalability and cost-efficiency of cloud-based solutions make them an attractive option for banks looking to modernize their IT infrastructure and improve service delivery.
Blockchain and chatbots represent longer-term investments for many banks. Blockchain technology is anticipated to achieve long-term adoption in 85.06% of banks, reflecting its potential to revolutionize transaction security and data integrity. Similarly, chatbots are projected to be fully developed in 37.2% of banks in the long term, aiming to automate customer service interactions and enhance customer engagement through AI-driven conversational tools.
These strategic plans demonstrate Albanian banks’ commitment to leveraging innovative technologies to enhance their operations and customer experiences. By balancing immediate needs with future aspirations, banks are positioning themselves to navigate the evolving digital landscape effectively and sustain their competitive edge in the financial sector.
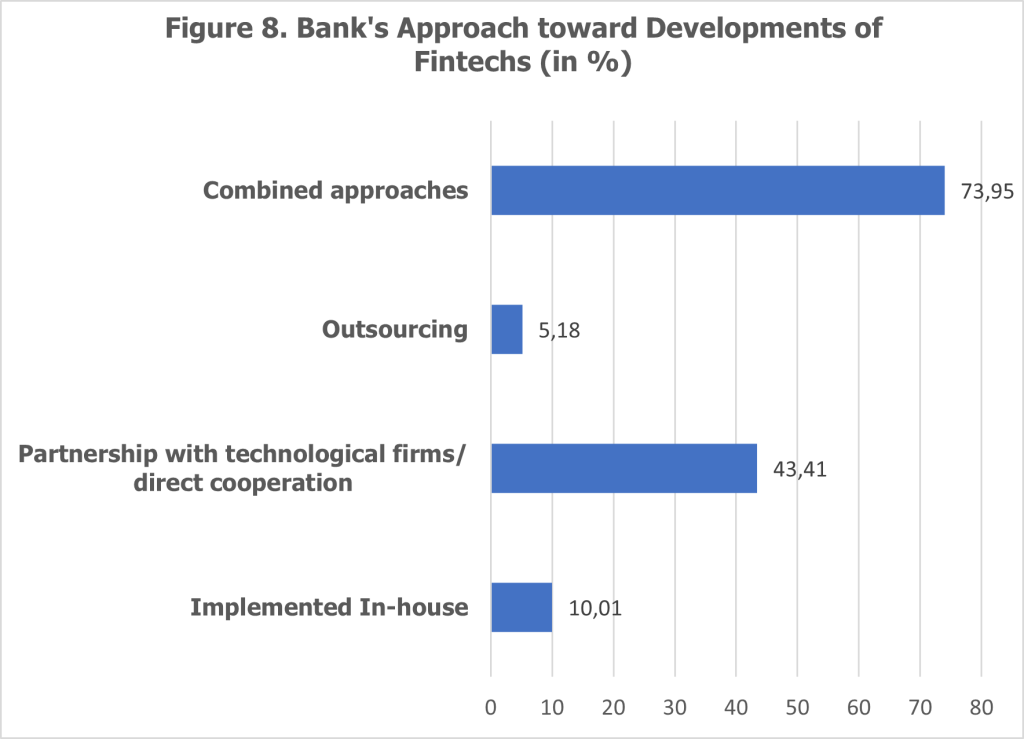
The implementation of FinTech projects by Albanian banks showcases diverse strategies to tackle the challenges of digital transformation (see Figure 8). One prominent approach is the combined model, adopted by 73.9% of banks, which balances in-house development with partnerships with technology firms. This hybrid approach allows banks to leverage external expertise for complex digital solutions while retaining control over core processes and sensitive data.
Partnerships with technology firms are another widely used strategy, with 43.41% of banks opting for direct collaborations. These partnerships provide access to specialized skills, advanced technologies, and accelerated time-to-market for FinTech solutions. However, concerns about data and financial security sometimes hinder the establishment of these collaborations, highlighting the need for enhanced trust and clear regulatory frameworks.
A smaller percentage of banks, approximately 10.01%, rely solely on in-house development to execute their digital projects. This strategy demonstrates confidence in their internal capabilities to design, implement, and manage FinTech solutions without external assistance. While this approach ensures full control over projects, it may limit access to innovative technologies and external expertise.
Outsourcing represents a niche strategy, utilized by 5.18% of banks. By outsourcing FinTech projects, banks tap into third-party expertise to drive innovation and execute digital initiatives efficiently. This approach is particularly beneficial for smaller banks with limited internal resources, although it may raise concerns about dependency on external vendors.
Partnerships with FinTech firms emerge as a critical enabler of successful digital transformation. Despite challenges in establishing these collaborations, proactive partnerships can help banks overcome significant barriers such as high implementation costs and limited internal expertise. From the central bank’s perspective, fostering these partnerships ensures that customer experience and competitiveness improve safely and sustainably, preserving stability across the financial system.
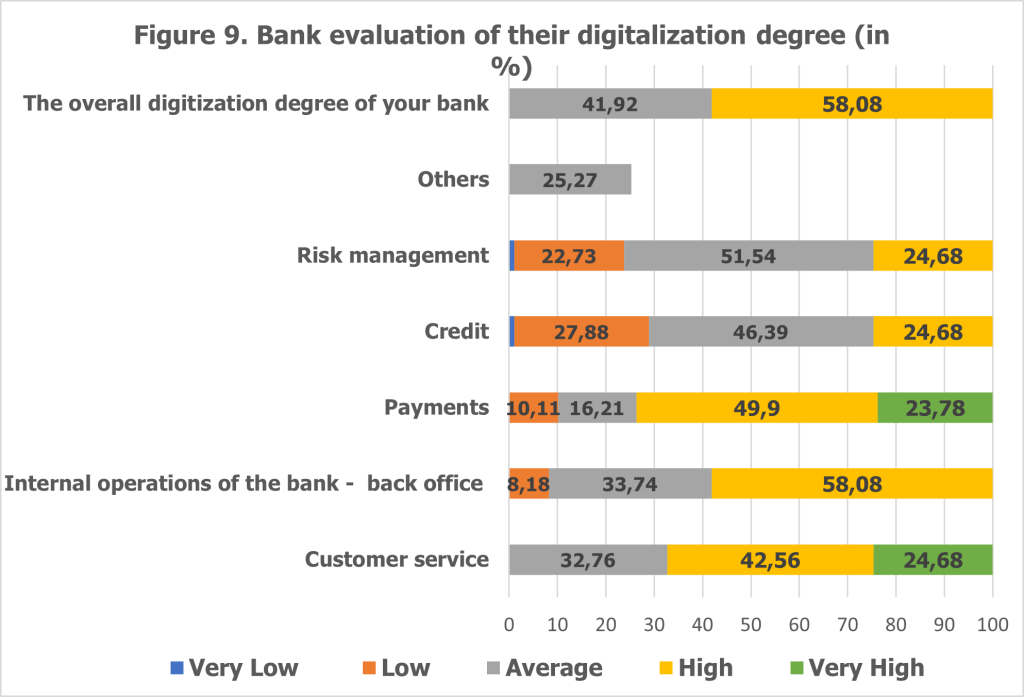
The survey assessed the degree of digitalization across different business areas within banks, providing valuable insights into the progress of digital transformation in the Albanian banking sector (see Figure 9).
Payments emerged as the most digitized area, with 23.78% of banks indicating a “very high” level of digitalization and 49.9% reporting a “high” level. This reflects global trends, where digital transformation efforts in banking often prioritize payment services due to their critical role in customer engagement and convenience.
Customer service follows closely, with 42.56% of banks rating the digitalization of this area as “high” and 24% as “very high.” This emphasis demonstrates the sector’s growing focus on enhancing customer experiences through digital channels and automation, addressing evolving customer expectations for seamless interactions.
Internal operations, particularly back-office functions, show moderate levels of digitalization. A significant 58.8% of banks rated this area as “high,” while a smaller segment (8.2%) reported “low” levels of digital adoption. Digital transformation in back-office processes is essential for operational efficiency and cost reduction, though some banks remain in the early stages of this transition.
Credit services and risk management are the least digitized areas, with 27.88% of banks rating the digitalization of credit services as “low,” and some even indicating a “very low” level. Similarly, risk management has experienced limited digital adoption, reflecting a cautious approach to these high-stakes areas where errors can have significant consequences.
Overall, 58.8% of banks rated their digitalization level as “high,” while 41.9% assessed it as “average.” These self-assessments highlight the sector’s ongoing journey towards a fully digitized operational framework, with substantial progress in some areas and opportunities for improvement in others.
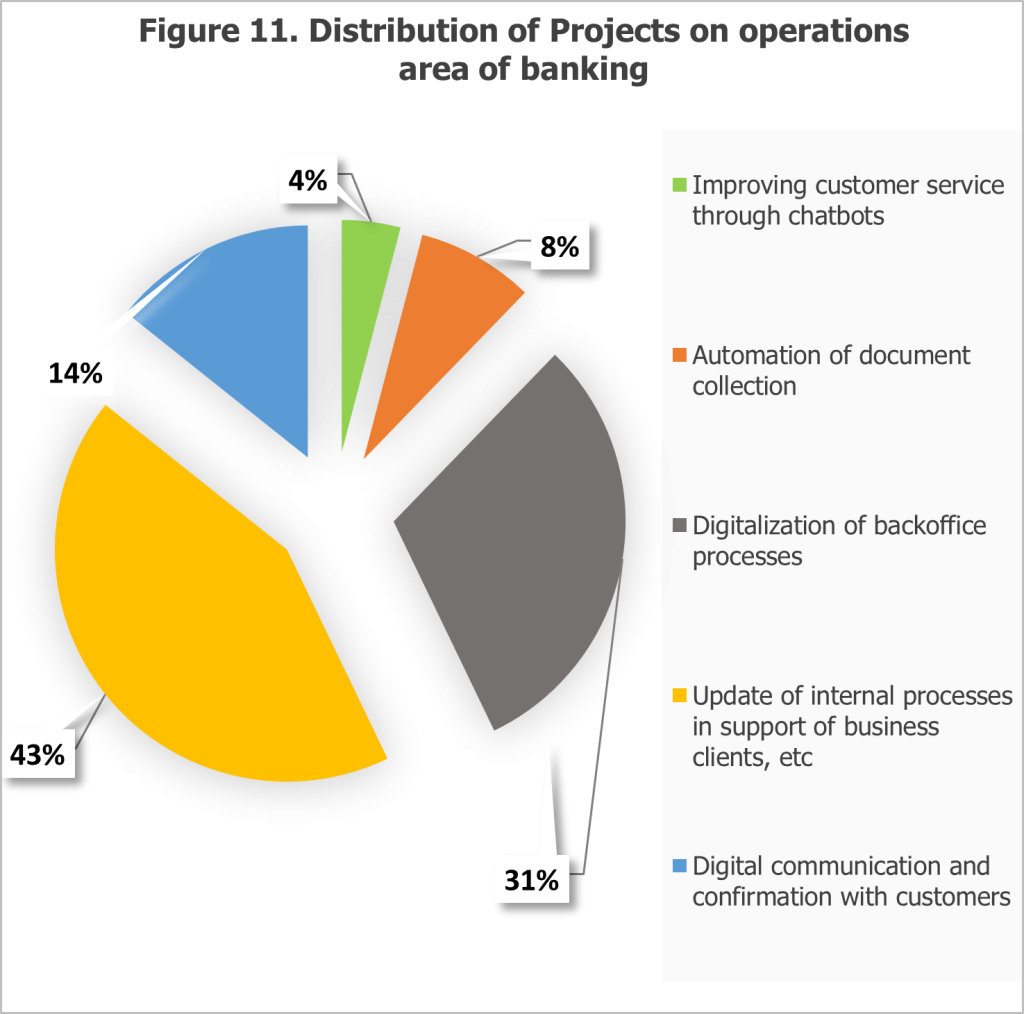
The survey also explored the specific areas where banks are implementing FinTech projects, offering insights into the focus areas for innovation (see Figures 10 and 11). The findings reveal that operations are the primary focus for FinTech initiatives, with 73 projects currently being implemented. Key projects in this area include digital communication and confirmation with customers, internal process updates for business clients, back-office process digitization, document collection automation, and chatbot integration to improve customer service. This concentration reflects the banking sector’s strategic emphasis on improving workflow efficiency, reducing manual processes, and enhancing service delivery.
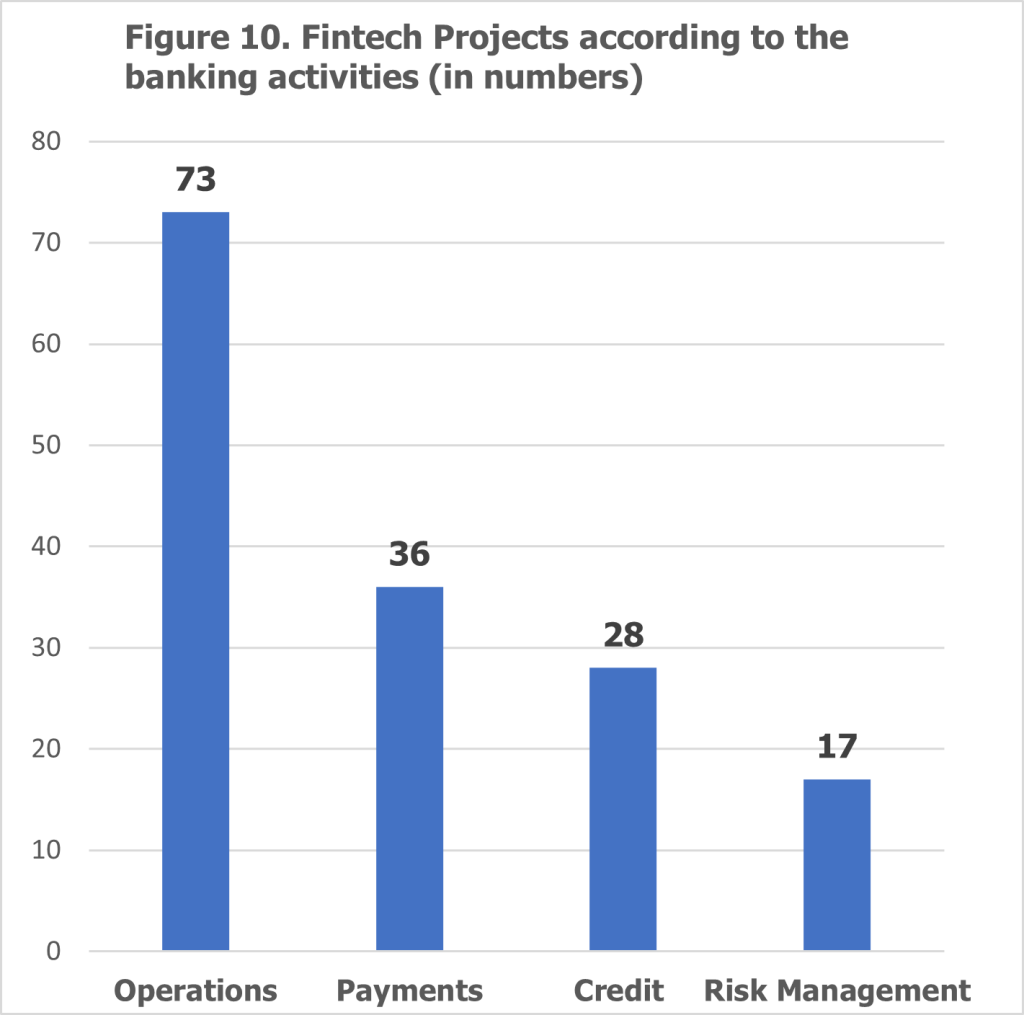
Payments account for 36 projects, highlighting the critical role of digital innovation in ensuring seamless, efficient, and secure transactions. As a cornerstone of customer engagement, payments remain a priority area for banks looking to enhance satisfaction and operational effectiveness through FinTech solutions.
The credit domain has seen 28 projects focused on automating and digitizing loan-related processes. While still in the early stages of digital transformation, initiatives in this area aim to streamline approval processes, leverage data-driven lending models, and improve the overall customer experience in credit services.
Risk management, with 17 projects, represents the least digitized area within banks. This limited focus may reflect the cautious approach adopted by banks in managing high-stakes activities, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards while balancing the potential risks of digital innovations. Nevertheless, there is significant scope for growth in leveraging digital tools to enhance risk assessment and mitigation strategies.
The emphasis on operational projects underscores the sector’s drive toward internal efficiency and process optimization. Investments in back-office automation, customer interaction tools, and workflow improvements demonstrate a clear commitment to productivity enhancements. Meanwhile, the focus on payments and credit highlights the importance of customer-facing innovations, while the slower adoption in risk management signals an opportunity for strategic development in this critical area.
Exploring the benefits of digital transformation is crucial, as it helps assess the tangible impact of digitization on the banking sector (see Figure 12). The survey highlights several key benefits that banks in Albania expect to gain from their digital initiatives.
Effectiveness of processes ranks as the most significant benefit, with 97.12% of banks “strongly agreeing” and 2.88% “agreeing” that digitization enhances banking operations. This efficiency includes faster, more streamlined workflows, enabling banks to serve customers better while reducing operational costs. Closely linked to process effectiveness is the improvement in accuracy. Automation of tasks such as customer onboarding, compliance reporting, and fraud detection reduces human errors and ensures more reliable service delivery. An impressive 87.59% of banks “strongly agree” that accuracy of actions is one of the most tangible benefits of digitalization.
Reducing transaction costs is another notable advantage, recognized by 63% of banks, although 24.6% expressed a neutral view, and a small percentage disagreed. This variability suggests that while digitization has the potential to cut costs, its realization depends on the specific implementation strategies and operational contexts of individual banks.
Enhanced customer choices and benefits also feature prominently among the reported advantages. Approximately 57.5% of banks “strongly agreed” and 42.5% “agreed” that digitization expands the range of services available to customers, offering personalized solutions and accessible digital platforms. These enhancements are critical for boosting customer satisfaction and retention.
Digitization is also seen as a driver of financial inclusion and European integration. Around 32.13% “strongly agree” and 62.7% “agree” that digital transformation allows a broader population to access financial services. Additionally, the alignment of digital initiatives with European integration goals is highlighted, with 64.8% agreeing and 25.03% strongly agreeing that digitization supports these efforts.
Lastly, digitization is recognized for its potential to expand market opportunities. Nearly half (49.7%) of banks agree that FinTech initiatives enable entry into previously unexplored areas, creating new business opportunities and fostering innovation in the financial sector.
By investing in digital transformation, Albanian banks can achieve significant benefits, including improved process efficiency, enhanced accuracy, reduced transaction costs, and expanded market reach. These advancements contribute to a more inclusive and competitive banking environment, positioning the sector for sustained growth and alignment with global financial trends.
Exploring the benefits of digital transformation is crucial, as it helps assess the tangible impact of digitization on the banking sector (see Figure 12). The survey highlights several key benefits that banks in Albania expect to gain from their digital initiatives.

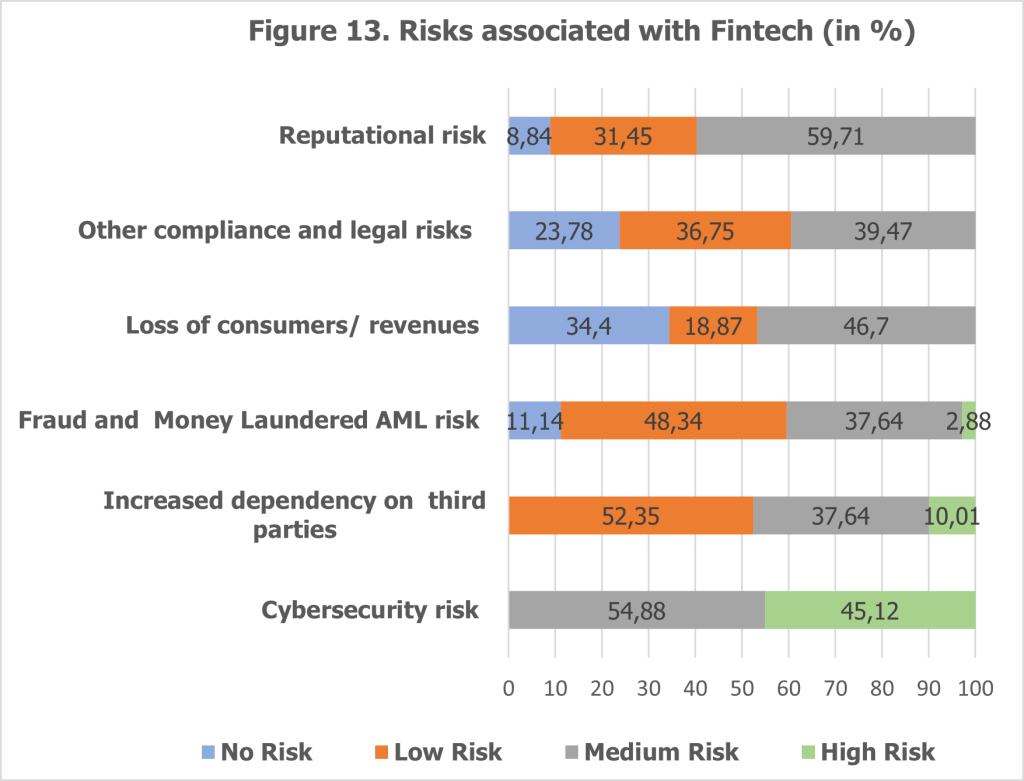
While digital transformation brings numerous benefits, it also introduces specific risks, particularly as banks adopt FinTech solutions (see Figure 13). Cybersecurity risks emerge as the top concern, with 45.12% of banks rating them as “high” and 54.88% considering them “medium.” As banks increasingly handle sensitive customer data, robust cybersecurity measures are essential to prevent data breaches and maintain customer trust.
Dependency on third parties is another significant risk, with 10.01% of banks identifying it as a high risk and 37.64% as a medium risk. Many banks partner with technology firms to drive innovation, but this dependency introduces vulnerabilities, especially if third parties face operational or security challenges.
Compliance and legal risks are also key concerns, as banks must navigate complex regulatory landscapes while ensuring that their digital initiatives adhere to legal standards. These challenges are amplified when collaborating with external technology providers, requiring robust governance frameworks to mitigate potential issues.
Fraud and money laundering risks are heightened in a digital environment. Advanced fraud detection mechanisms are critical to addressing these threats. The survey reveals that 37.6% of banks consider fraud risks as “medium” while 2.88% categorize them as “high.” This highlights the importance of investing in sophisticated tools to combat financial crimes.
Reputational risks are another concern, with 59.7% of banks assessing them as “medium” and 8.84% viewing them as “low.” Any disruption, such as data breaches or service failures, can damage a bank’s reputation, eroding customer trust and potentially leading to financial losses.
Interestingly, the risk of losing consumers or revenue was considered negligible by 34.4% of banks, categorized as “no risk,” while 18.87% saw it as a “low risk.” This suggests that while customer retention is a concern, many banks remain confident in their ability to navigate digital transformation without significant client attrition.
In summary, while FinTech adoption offers substantial benefits, banks must proactively address associated risks through comprehensive strategies, including enhanced cybersecurity measures, robust regulatory compliance, and strategic partnerships with third-party providers. These efforts are essential to ensure a safe and sustainable digital transformation journey in the Albanian banking sector.
When asked about their readiness to address cyber risks associated with FinTech, Albanian banks demonstrated significant confidence in their preparations (see Figure 14 and 15). Approximately 65.33% of banks rated themselves as “very prepared,” while an additional 30.74% indicated they were “prepared.” This self-assessment underscores the proactive measures undertaken by banks to strengthen their cybersecurity frameworks as part of their digital transformation journey.
The survey results reflect a strong emphasis on adopting advanced cybersecurity protocols and investing in robust systems to safeguard customer data and banking operations. Despite this confidence, a small percentage of banks (3.93%) rated their readiness as “average,” highlighting areas where additional focus might be required. Ensuring comprehensive cybersecurity preparedness is critical, as the increasing reliance on digital platforms exposes banks to evolving threats, necessitating constant vigilance and adaptation.
Moreover, the survey revealed that 77.95% of banks had experienced cybersecurity incidents, while 22.05% reported no such occurrences. These findings suggest that while a majority of banks have successfully mitigated risks thus far, the occurrence of incidents in a subset of institutions underscores the need for continuous improvement in cybersecurity measures.
By maintaining a proactive stance and addressing potential vulnerabilities, Albanian banks can build resilience against cyber threats, ensuring the trust and security of their customers as they navigate the complexities of the digital era.
In parallel with the increasing demand for digital financial services, the exposure of banks and their customers to cyberattacks is also rising. As a consequence of various financial services and, as well as the internal processes of banks shifting more and more to the digital space, cyber threats appear as a new type of risk. As banks increasingly adopt digital financial services, they also face a higher risk of cyberattacks, which represent a new type of threat in the digital era (see Figure 15).

The rise of FinTech and digital transformation in the banking sector has brought with it an inevitable increase in cybersecurity concerns. According to the survey, approximately 78% of Albanian banks reported experiencing some form of cyber incident, while the remaining 22% stated they had not encountered such issues (see Figure 15). These findings highlight the growing importance of cybersecurity as a critical component of digital transformation strategies.
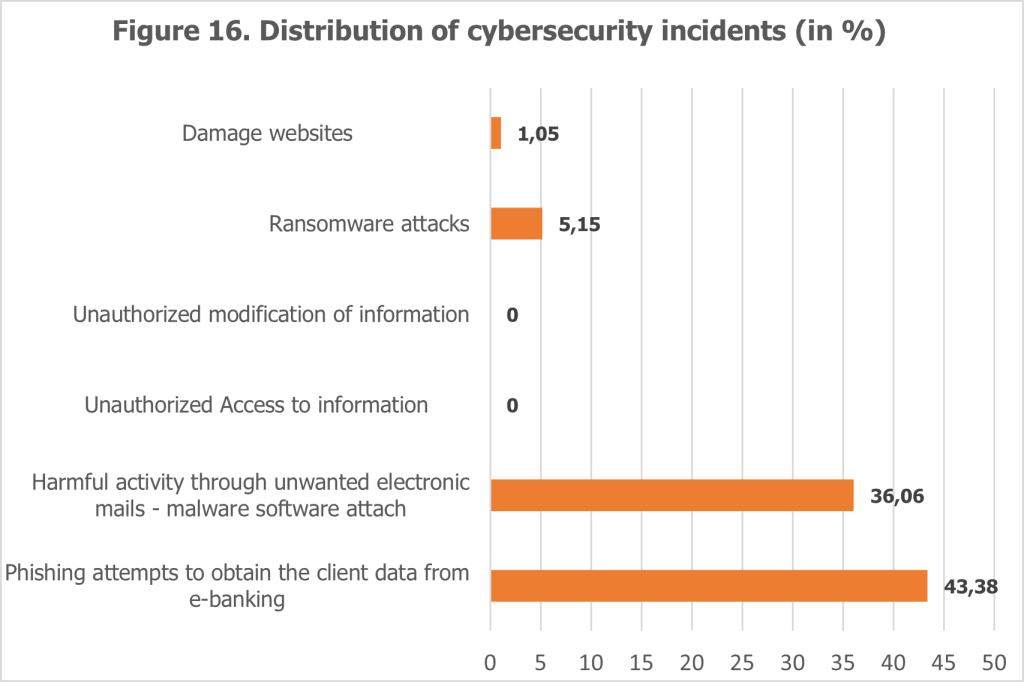
Phishing attempts were identified as the most prevalent cybersecurity incident, targeting customers to obtain sensitive information such as internet banking credentials and credit card details. These attacks often take the form of emails that mimic official bank communications, complete with logos and branding, and include links to fraudulent websites or malware downloads. The widespread nature of phishing attempts underscores the need for banks to adopt robust detection and prevention mechanisms to protect their customers from such threats (see Figure 16).
In addition to phishing, banks reported instances of harmful electronic communications that resemble legitimate emails. These emails aim to mislead clients by including fake links or attachments, ultimately compromising data security. This type of activity not only threatens the security of customer information but also undermines trust in digital banking services.
Less common but still notable were incidents involving unauthorized access attempts, ransomware attacks, and unauthorized data modifications. These more sophisticated threats, while less frequent, underscore the importance of maintaining comprehensive cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive financial data and ensure operational integrity.
Interestingly, one bank commented that phishing attempts, while a constant challenge, have not shown a significant increase directly linked to new digital initiatives. This suggests that despite the heightened risks associated with digital transformation, Albanian banks are largely effective in managing these challenges. Nevertheless, as digital banking services expand and become more complex, the need for continuous improvement in cybersecurity practices remains paramount.
By investing in advanced security technologies and fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness, banks can mitigate these risks, ensuring a safe and secure environment for customers and operational processes alike. These efforts are essential to sustain the trust of customers and stakeholders in the digital banking ecosystem.
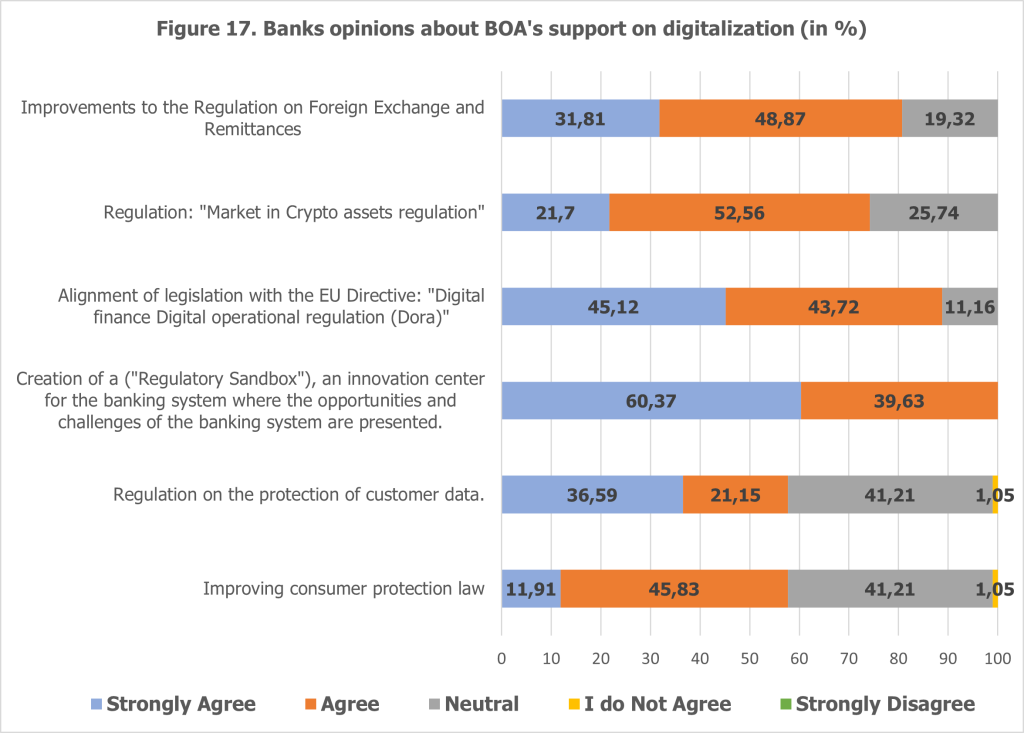
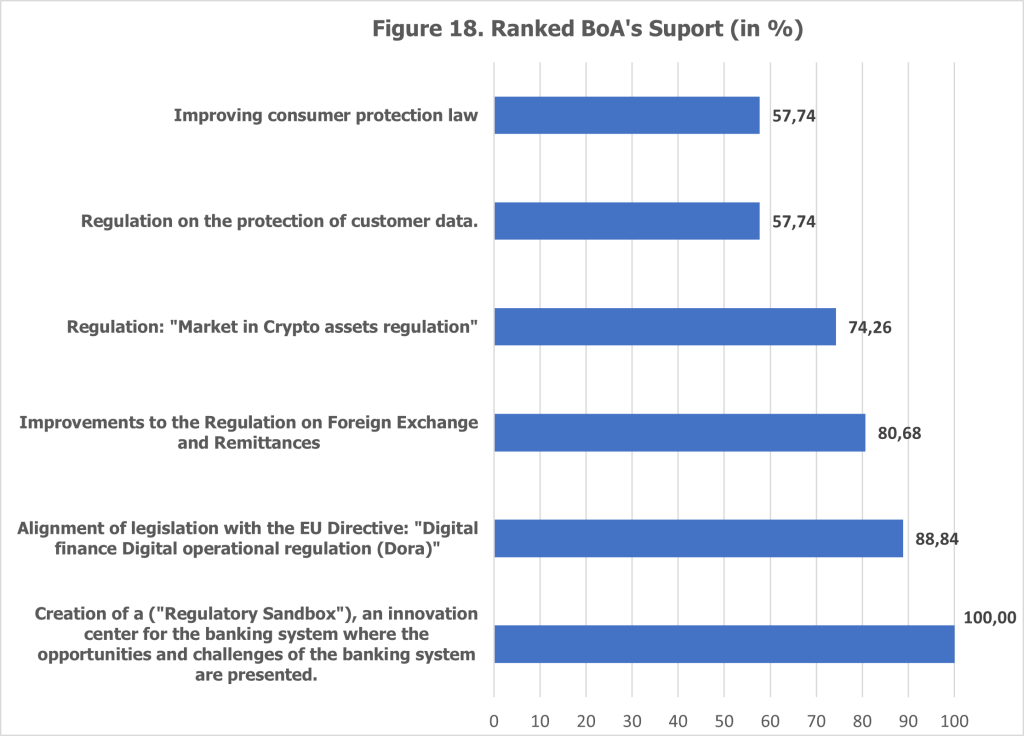
The Bank of Albania (BoA) holds a pivotal position in fostering the digital transformation of the banking sector in Albania. Insights from the survey revealed a consensus among banks on several critical areas where the central bank’s intervention and support could significantly accelerate the pace of digitalization and enhance its overall effectiveness (see Figures 17 and 18).
One of the most prominent recommendations was the creation of a Regulatory Sandbox. This initiative was universally endorsed by all participating banks, with 60.4% “strongly agreeing” and the remaining 39.6% “agreeing” on its necessity. A Regulatory Sandbox provides a controlled environment where banks can test and refine innovative digital solutions while managing associated risks effectively. This initiative would not only promote innovation but also serve as a platform for banks to collaborate with regulators, ensuring compliance while addressing the unique challenges posed by digital transformation.
Alignment with EU Directives emerged as another priority, particularly the Digital Finance and Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA). Nearly 45.12% of banks “strongly agreed” and 43.72% “agreed” that aligning Albanian regulations with European standards is essential. This alignment would facilitate cross-border operations, enhance regulatory compliance, and enable Albanian banks to operate seamlessly within the broader European financial ecosystem.
The improvement of regulations surrounding foreign exchange and remittances also stood out as a critical area for BoA’s support. Approximately 31.81% of banks “strongly agreed” and 48.8% “agreed” on the importance of modernizing these regulations. Given the significant role of remittances in Albania’s economy, enhanced frameworks in this domain would streamline processes, reduce transaction costs, and improve service efficiency for customers.
Other areas of support highlighted by the banks include the regulation and protection of customer data, which is essential for safeguarding sensitive information in an increasingly digital financial landscape. Additionally, stronger consumer protection laws were cited as crucial for building trust in digital services and ensuring equitable treatment of customers in this new financial era. The regulation of crypto assets also surfaced as an area requiring BoA’s guidance, with banks requesting clear directives to integrate these assets into the financial ecosystem responsibly.
By addressing these key areas, the Bank of Albania can act as a catalyst for the country’s digital transformation, ensuring that innovation is implemented within a secure and regulated framework. This proactive approach will not only strengthen the resilience and competitiveness of the Albanian banking sector but also align it more closely with international standards and expectations.
The digital transformation of Albania’s banking sector, transitioning from traditional to digital services, reflects a pivotal shift driven by evolving customer behavior, the necessity to attract new generations of customers, the imperative to safeguard data from cyber threats, and the increasing demand to remain competitive in a FinTech-driven landscape. Digitalization is no longer an option but a structural trend, prompting a move from product-centric to customer-centric business models across the sector.
The payments sector, as the most digitalized area in Albanian banking, showcases the initial stages of FinTech development. However, the journey of digital transformation is ongoing and demands continuous adaptation to technological advancements across all areas of banking. This survey highlights that Albanian banks have adopted a collaborative approach, engaging with technology firms to propel their digitalization strategies forward.
Technologies such as mobile banking, Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), e-banking, and biometric verification have become foundational pillars of this transformation. Simultaneously, emerging innovations like cloud computing, digital wallets, and chatbots are expected to play a more significant role in the medium term. Mobile banking, in particular, stands out as a cornerstone of the digital banking experience, universally adopted by all banks in Albania. By enabling customers to access and manage their finances conveniently, mobile apps have enhanced customer satisfaction, engagement, and loyalty, solidifying their role as an indispensable tool in modern banking.
Nevertheless, the proliferation of digital channels—including mobile applications, online banking portals, and chatbots—also increases exposure to cyber threats. Addressing the rising risk of cyberattacks and data breaches is imperative. Banks must prioritize implementing robust security frameworks to protect sensitive customer information from exploitation by cybercriminals. Ensuring a secure digital environment is fundamental to maintaining customer trust and fostering the continued adoption of digital banking services.
Beyond security, there is a growing call for the Bank of Albania to spearhead initiatives aimed at enhancing digital literacy and financial awareness among the population. Improved financial education would foster broader adoption of digital services, advancing financial inclusion across Albania. Additionally, banks have expressed unanimous support for the establishment of a Regulatory Sandbox, which would serve as an innovation hub for the banking sector to test and refine new technologies in a controlled environment.
Ultimately, digital transformation in banking extends beyond the mere adoption of new technologies; it represents a profound evolution in how banks engage with and meet the needs of their customers. To navigate this transformation successfully, banks must take strategic measures to strengthen their technological infrastructure, remain adaptable to customer preferences, and foster innovation. With a steadfast commitment to these goals, Albania’s banking sector is poised to build a future-ready industry capable of meeting the demands of the digital era while fostering trust, inclusion, and innovation.
Boot, A., Hoffmann, P., Laeven, L., & Ratnovski, L. (2020). Financial intermediation and technology: What’s old, what’s new? ECB Working Paper Series No. 2438. European Central Bank. https://www.ecb.europa.eu/pub/pdf/scpwps/ecb.wp2438~d0d447b9b6.en.pdf
Magyar Nemzeti Bank. (2020). Fintech and digitalisation report 2020. https://www.mnb.hu/en/publications/reports/fintech-and-digitalisation-report
European Central Bank. (2024). Digitalisation: Key assessment criteria and collection of sound practices. https://www.bankingsupervision.europa.eu/ecb/pub/html/ssm.reportondigitalisation_202407~3f4de7a771.en.html
National Bank of the Republic of North Macedonia. (2020). FinTech survey 2020. Sponsored by EFSE Technical Facility. https://www.nbrm.mk/content/RNM%20Fintech%20Survey%20Final%20Report%20Clean%20211220.pdf
European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA). (2022). Digital finance related issues – Survey to NCAs. (ESMA50-164-5411). https://www.esma.europa.eu/sites/default/files/library/esma50-164-5411_digital_finance_survey_to_ncas.pdf
Bank of Italy. (2023). The results of the fourth FinTech survey conducted by the Bank of Italy during 2023. https://www.bancaditalia.it/media/notizia/indagine-fintech-nel-sistema-finanziario-italiano-2023/
FinTech projects represent investment initiatives focused on technological and financial innovation capable of generating new processes, products, services and business models. The list and description of the technologies are contained in the methodological note.
https://thedocs.worldbank.org/en/doc/b30a11542af1788a53df6bb660d9b41e-0050062022/original/Data-for-Figures-Ch-2.xlsx.
As the Regional overview of internet usage by ITU Facts and figures for 2022 (Source: https://www.itu.int/itu-d/reports/statistics/facts-figures-2022/)
One bank of the system is not responded this question.