

The sharp rise in public debt-to-GDP ratios in the aftermath of the financial crisis of 2008 posed serious challenges for fiscal policy in the euro area countries and culminated for some member states in a sovereign debt crisis. This note examines the public policy responses to the euro area crisis through the lens of financial repression with a particular focus on how they contributed to easing government budget constraints. Financial repression is defined in this context as the government’s strategy – supported by monetary and financial policies – to gain privileged access to capital markets at preferential credit conditions and divert resources to the state with the aim to secure and, if necessary, enforce public debt sustainability.Following a narrative approach, this note finds that public debt management and resolution, European financial legislation, EMU crisis support and ECB monetary policy have significantly contributed to relieving sovereign liquidity and solvency stress and generated fiscal space through non-standard means. The respective authorities have in fact applied the tools of financial repression to restore stability after the euro area crisis.
1. Introduction
The sharp rise in public debt-to-GDP ratios in the aftermath of the financial crisis of 2008 posed serious challenges for fiscal policy in the euro area countries. Euro area governments have undertaken a range of countervailing and confidence-building measures, focused on fiscal consolidation, asset privatisation and structural reforms, in addition to measures to improve the resilience of the banking sector and break the sovereign-bank nexus at the national level.
Apart from these standard responses to fiscal stress, history suggests that crisis-hit countries might also turn to non-standard financial repression techniques in an effort to stabilise public finances, i.e. a suite of coercive measures imposed on the financial and monetary system – exploiting national regulators and the central bank – to gain privileged access to capital markets at preferential credit conditions and to divert resources to the state (see Reinhart et al., 2015).2 The main purpose of financial repression from a fiscal perspective is to sustain debt financing at affordable interest rates but it may also entail a confiscation of assets to reduce a debt overhang. These capital market interventions could be vital to restore the state’s debt issuing capacity and thus its ability to implement a fiscal stimulus.
Considering the historical experience, these short-term fiscal advantages of financial repression could come at significant longer-term costs. Since a financial repression regime circumvents or undermines market-based budgetary discipline, the government could decide to postpone or put off standard measures of fiscal retrenchment, leaving the overhang of public debt unaddressed. Pressing financial institutions to hold more own sovereign debt makes them vulnerable to adverse fiscal shocks that lead to valuation losses and weaken their balance sheets. A privileged capital market access for the public sector may crowd out private borrowers and, hence, translate in a lower potential growth path of the economy. Moreover, monetary policy interventions in the sovereign bond market aimed at keeping interest rates low on a protracted basis could cause a low-quality capital structure, spur excessive risk-taking, and entail a redistribution of income from savers to borrowers. Hence, financial repression raises questions of economic efficiency, financial stability and political legitimacy.
This note examines the policy responses to the euro area crisis through the historical lens of financial repression with a focus on the consequences for public finances (see also van Riet, 2018). The question is whether and how the authorities have applied financial repression methods again in modern times and as a result – intended or unintended – relieved fiscal stress. The note reviews in turn national public debt management, European financial governance, official sector support and public debt resolution, and the ECB’s monetary policy interventions (Sections 2 to 5). The conclusion is that these crisis-related public policies were targeted at restoring euro area stability but also generated significant fiscal benefits (Section 6). This could signal a new “age of financial repression” (Eijffinger and Mujagic, 2012).
2. National public debt Management
Membership of the Economic and Monetary Union (EMU) removes a country’s control over monetary policy and the exchange rate and constrains the set of tools that it has available to respond to a negative shock. A crisis that feeds market fears of a sovereign default and euro exit may quickly trigger capital outflows and higher interest rates. Due to contagion effects even a solvent euro area country could see a liquidity crisis quickly turning into a self-fulfilling default (De Grauwe, 2012; Eijffinger et al., 2018).
Euro area governments affected by the sovereign debt crisis accordingly looked for ways to ease their liquidity and solvency constraints by more actively managing both the supply and demand of government debt in response to the sudden retreat of foreign investors and rapidly rising sovereign bond yields. On the one hand, public debt managers tried to make issuance conditions more attractive and better attuned to domestic audiences to secure continued market access at affordable interest rates (Hoogduin et al., 2011; Holler, 2013). On the other hand, several euro area countries embraced certain aspects of financial repression to attract a higher interest in low-cost sovereign debt from a captive domestic investor base.3
At the start of the sovereign debt crisis, financial repression mainly showed up in unusual forms of public debt management. Domestic banks faced supervisory pressure to repatriate funds from abroad and moral suasion to invest in bonds issued by their own government (Ongena et al., 2016). They were also confronted with political pressure to take advantage of cheap ECB liquidity offered at an unusual three-year maturity and to park these funds in national government bonds. After the earlier relaxation of eligibility criteria, lower-rated sovereign debt securities could still be pledged as collateral in the ECB’s credit operations, albeit with a discount. Sometimes, temporary ceilings placed on the remuneration of retail bank deposits created incentives for savers to shift their wealth into government bonds.
Also pension funds and insurance corporations were subject to moral suasion and regulatory pressure, pushing them to invest more at home, in particular in public debt. A few crisis-hit countries used the reserves accumulated by pension funds to fill holes in the government budget and to limit the need for official financial assistance. Furthermore, taxes on financial transactions and administrative controls constraining the free functioning of securities markets introduced barriers against speculation and often also promoted investment in government bonds.
Figure 1: Ownership of euro area government debt and interest payments, 1995-2016
(percent of GDP)
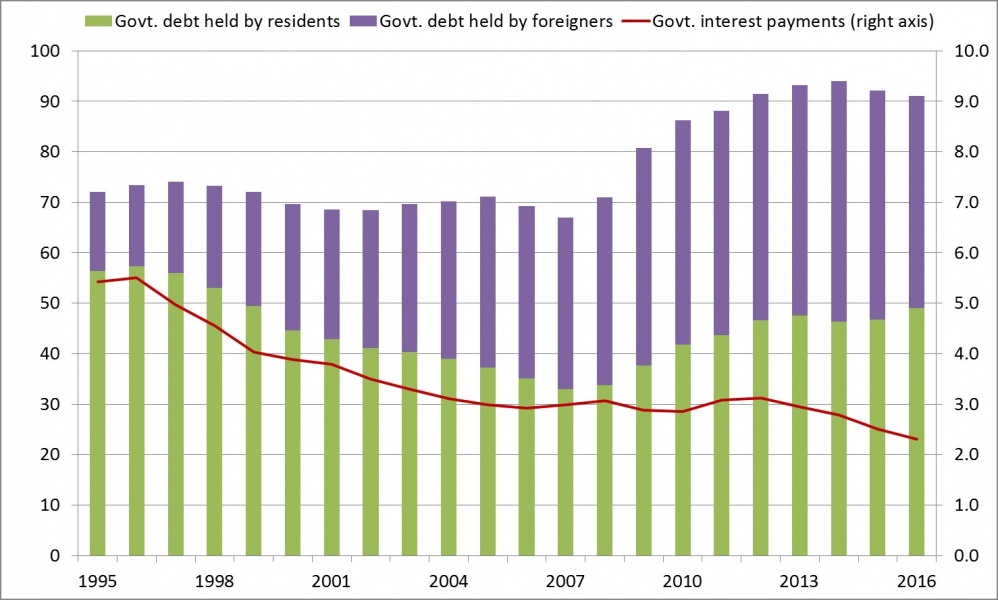
Source: ECB and Eurostat.
Note: Euro area comprises the first 12 member countries. Government debt is defined in gross terms and consolidated across general government. The concept of resident/foreign owners of debt applies at the national level.
Public debt management operations had a significant impact on the contribution of domestic investors to the financing of euro area government debt (Figure 1). Over the first 10 years of the euro’s existence, the share of non-residents in total government debt showed a steady rise and that of residents accordingly declined, especially for smaller member countries. With the onset of the euro area crisis, this trend has gone into reverse, notably in the crisis-affected countries. This reversal may reflect both economic considerations (the sell-off by foreign investors and the greater attractiveness of public debt to domestic audiences) as well as the application of financial repression techniques to resident investors under political control (De Marco and Macchiavelli, 2016) that leads to an artificial home demand for government debt securities and helps to contain the rise in debt interest payments.
3. European financial governance
The European Banking Union with its centralised banking supervision and resolution as well as Europe’s action plan for a Capital Markets Union constrain the ability of national authorities to repress the financial sector and domestic capital markets (Ve ron, 2012, 2014). At the same time, a growing body of European legislation that was introduced over the period 2008-2017 to promote a sound financial sector and enhance financial stability also contributes to easing governments’ access to capital on a structural basis.
The crisis-induced home bias discussed above was further supported by the preferential treatment of government debt in revamped EU financial sector legislation. EU prudential banking law (the Capital Requirements Regulation and Capital Requirements Directive IV) offers supervisors ample opportunity to allow the banks in their jurisdiction to consider all their claims on Member States denominated and funded in the domestic currency as high-quality and liquid assets free of credit risk against which in most cases no capital or liquidity buffers need to be maintained, irrespective of the size of the sovereign exposure. This favourable treatment of public debt stands in contrast with the strict prudential requirements for bank holdings of corporate debt and it preserves an artificial level of demand for debt issued by less creditworthy governments. The corresponding sovereign funding privilege is of particular advantage to euro area countries, since they share the same currency and therefore can attract credit institutions from the whole monetary union on equal regulatory conditions.4
Government funding privileges can also be found in EU prudential legislation for other parts of the financial sector. Under the new Solvency II directive, insurance companies must hold adequate capital against an array of risks related to their investments: the so-called Solvency Capital Requirement. However, the standard calculation formula assigns a capital exemption to claims on or guaranteed by European governments issued in their own currency with regard to market risks associated with spread risk (i.e. the sensitivity to credit spreads over the risk-free interest rate) and concentration risk (i.e. a large exposure to default of a counterparty or the lack of asset diversification). Such sovereign risks are only covered by the need for insurance companies to undertake an adequate own risk and solvency assessment.
Furthermore, the revised EU investment funds directive (UCITS IV) gives the national competent authorities, as before, considerable freedom to authorise collective investment undertakings to invest sizeable amounts in transferable securities and money market instruments that are issued or guaranteed by single public sector bodies in Europe. The applicable concentration limits may be waived and the counterparty exposure limit for sovereigns far exceeds those for private issuers.
The EU regulation on money market funds contains similar derogations with regard to concentration limits and diversification requirements for money market instruments issued or guaranteed by central governments, which are always assumed to be eligible liquid assets of high credit quality. A favourable assessment of their eligibility is also not needed. This preferential treatment of public sector versus private sector issuers is partly mitigated by the requirement that money market funds undertake sound stress tests and must have prudent and rigorous procedures in place for managing their total liquidity risk and are able to deal with redemption pressures. European money market funds that aim to maintain a constant net asset valuation per unit of share (so-called CNAV funds) are no longer allowed to invest in private debt instruments but only in public debt. The presumed quality and liquidity of sovereign assets is expected to mitigate the systemic risk from potential investor runs. The European Commission has been requested to report within five years on the role of money market funds in public debt markets and the feasibility of establishing a quota whereby at least 80% of the assets of these CNAV funds are to be invested in EU public debt instruments.
The European Market Infrastructure Regulation (EMIR) seeks to allay the financial stability concerns related to transactions in derivative markets such as credit default swaps. This market regulation demands central reporting of all derivative contracts and central clearing of standardised over-the-counter derivative transactions through a recognised counterparty. The necessary posting of high-quality liquid collateral to cover the exposure to clearing parties in principle raises the regulatory demand for sovereign bonds. At the same time, EMIR exempts official public debt management operations. Moreover, the central counterparties are required to observe similar capital adequacy rules as banks and, hence, the same preferential regulatory treatment of their claims on European sovereigns applies as discussed above.
European capital market legislation shows attempts to silence market voices of concern about fiscal developments, leading to more subdued government interest rates. New EU regulations prohibit investors from purchasing uncovered sovereign default protection, introduce restrictions on the short-selling of government bonds and impose supervisory constraints on agencies issuing sovereign credit ratings. Moreover, the proposed common financial transactions tax through which 10 euro area countries plan to fight speculative market activity might exempt trading in government bonds and in that case would create a further sovereign funding privilege in addition to the extra public revenues that it generates.
4. Official sector support and public debt Resolution
To safeguard financial stability in the euro area as a whole, the European authorities established stabilisation mechanisms that offer market access support, precautionary credit lines and temporary loans to help governments facing liquidity stress. With the aim to counteract the related moral hazard, they introduced contractual arrangements that should enable insolvent euro area countries to resolve their public debt overhang in an orderly fashion.
Several euro area countries received conditional EU/IMF loans after having lost access to the capital market in order to help them bridge their gross borrowing needs until they had credibly adjusted their economy and regained investor confidence (Figure 2). As observed by Corsetti et al. (2017), the terms of official lending were eased several times in interaction with public debt sustainability concerns and market access constraints, leading to the granting of higher loan volumes, lower financing costs, longer maturities, deferred interest payments and extended grace periods. The significant budgetary savings and the smoother refinancing profiles due to this form of debt relief contributed to declining sovereign bond yields and helped the programme countries to return to the capital market.
Considering public debt resolution, as Greece received its first EU/IMF financial support package in May 2010, euro area finance ministers initially called on their domestic banks to share the funding burden and tried to persuade them to hold on to the impaired Greek government debt (Bastasin, 2015). Later on, as the sovereign debt crisis spread to other euro area countries, the Treaty establishing the European Stability Mechanism (ESM) laid down the principle of considering burden sharing between the private sector and the official sector to close the financing gap for exceptional cases of stability loans to a country in need of debt restructuring. Moreover, the ESM was given the status of preferred creditor after the IMF. Greece retrofitted a collection action clause based on domestic law in its outstanding bond contracts and organised a public debt restructuring in March 2012 involving a substantial haircut in connection with a second EU/IMF financial support programme. Private creditors faced strong political pressure to accept this offer in return for significant sweeteners (see also Zettelmeyer et al., 2013).
Figure 2: Official sector claims on euro area governments, 1999-2018
(percent of GDP)
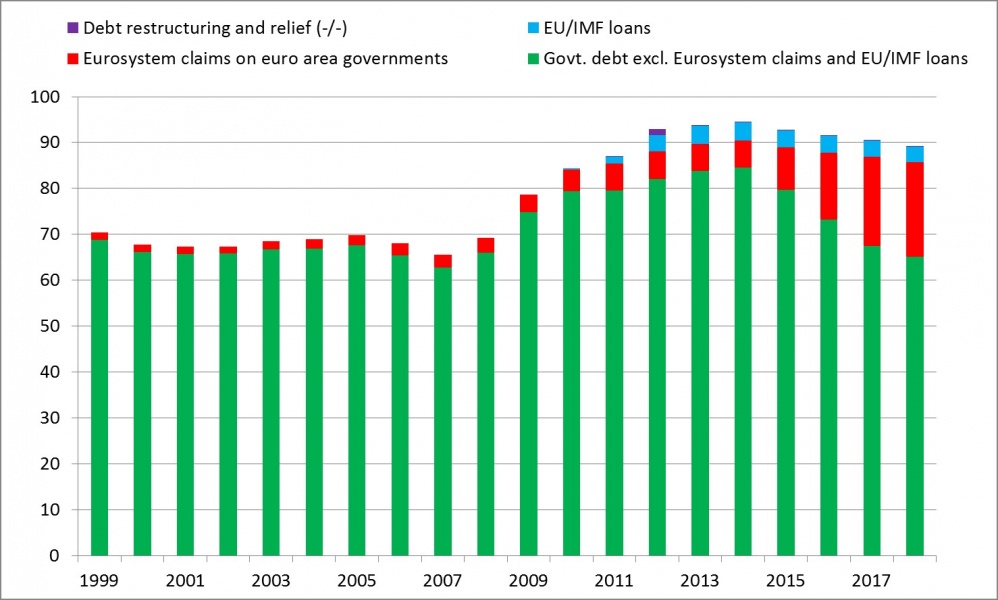
Source: ECB, Eurostat, and European Commission economic forecast of spring 2017.
Note: Euro area in changing composition.
When in spring 2015 a third financial support package was negotiated the Greek government demanded a cancellation of unsustainable debt owed to official creditors and organised a referendum in which the proposed austerity and reform conditions were rejected. Given the heightened risks of a financial meltdown, the Greek authorities had to impose temporary restrictions on financial transactions and capital outflows. Although Greece reached agreement with its European official lenders in August 2015, the IMF refused to join in with further financial assistance because it judged that the Greek fiscal position was not sustainable without first getting debt forgiveness from its euro area partners. Meanwhile, the Eurogroup has endorsed short-term solutions including maturity extensions and interest deferrals leading to a smoother debt repayment pro-file and more favourable debt dynamics (ESM, 2017). Moreover, it has committed to medium-term debt relief and contingency measures, if needed to ensure the long-run debt sustainability of Greece after it has successfully completed its third adjustment programme.
Cyprus was under pressure from its European partners to resolve a banking crisis at the lowest cost for taxpayers in order to limit the scale of official financial assistance. The national authorities therefore agreed in March 2013 to impose a one-off stability levy on both insured and uninsured bank deposit holders in return for an uncertain promise of future compensation. After its national parliament had rejected this confiscation as unconstitutional, the government decided instead to bail-in the shareholders and creditors of the two unviable systemic banks, while protecting the value of insured retail deposits up to EUR 100.000. Cyprus also had to place temporary restrictions on bank transactions, deposit withdrawals and capital outflows in order to counter a bank run and sustain a captive domestic investor base. Substantial capital flight would also have complicated the government’s return to the capital market.
To facilitate a potential future public debt restructuring at the expense of private creditors, eu-ro area countries are including as from January 2013 euro area collective action clauses (CACs) in the terms and conditions of government bond series. These should allow all debt securities issued by a country to be considered together in negotiations and thus make it easier to get a qualified majority of bondholders to accept a debt restructuring offer rather than to hold out against it.5 On the one hand, this expropriation risk should be expected to lead investors to demand a higher credit risk premium in interest rates. On the other hand, market participants might reward the lower costs of dealing with hold out creditors with a yield discount. A material impact of the introduction of CACs on government bond yields was not noticeable; if anything, those euro area countries with the weakest fiscal positions enjoyed slightly lower interest rates (Bradly and Gulati, 2014; Große Steffen and Schumacher, 2014). Hence, the CACs were ineffective in countering the moral hazard arising from countries now having the option to request conditional support and debt relief from the ESM.
5. The ECB’s monetary policy interventions
The sovereign debt crisis and the consequent market access difficulties for affected governments also caused a growing fragmentation of euro area financial markets along national lines, which seriously impaired the monetary transmission mechanism. The ECB responded with interventions aimed at repairing the dysfunctional securities markets, which helped to keep rising government bond yields of crisis-hit countries in check.
First, the ECB decided in May 2010 to intervene under its Securities Markets Programme, buying limited amounts of the government bonds of Greece, Ireland and Portugal, and later of Italy and Spain, in an effort to stabilise their debt markets and restore a smooth operation of the monetary transmission mechanism. Second, the ECB president pledged in July 2012 to do “whatever it takes” to preserve the euro, within the limits of the ECB’s mandate, after market participants increasingly called the continued existence of the euro into question. This statement was followed by an ECB commitment to undertake conditional but unlimited Outright Monetary Transactions in disrupted government bond markets in case monetary concerns justified such an intervention. As a result, crisis-hit countries saw their government bond yields declining substantially and their previous self-fulfilling default expectations were neutralised.
As inflation expectations started sliding down in 2014, ECB monetary policy turned to fighting low inflation in the euro area. Money market rates were moved slightly into negative territory to exploit the remaining scope for a standard cut in key interest rates up to the effective lower bound. Non-standard credit operations, quantitative easing measures and forward guidance on the monetary stance remaining accommodative engineered a substantial decline in euro area average longer-term interest rates as well as a significant reduction of government bond spreads. The aim of the ECB’s exceptional monetary accommodation was to ease private financing conditions and reflate the euro area economy. As a by-product, it translated into significant budgetary advantages.
The successful monetary policy efforts to prevent deflation avoided an undue rise in the real value of public debt. Higher GDP growth and falling unemployment boosted tax revenues as a source of debt service payments and reduced primary (i.e. non-interest) expenditure. Government interest payments declined to a low level, also because public debt managers used the opportunity of ultra-low bond yields to lengthen the maturity of new debt issues. By late 2018, the Eurosystem will hold some 20% of GDP in debt securities issued by euro area governments on its balance sheet (Figure 2). The net interest received on its growing monetary policy portfolio of public and private sector bonds allowed national central banks to strengthen their financial buffers and to make extra remittances to their governments.
6. Conclusions
This note finds that public debt management and resolution, European financial legislation, EMU crisis support and ECB monetary policy have greatly supported euro area governments in dealing with their fiscal predicament. Taken together, these public policy interventions contributed to a steadily declining implicit interest rate paid over the outstanding stock of public debt relative to nominal GDP growth (Figure 3) and helped to secure or enforce public debt sustainability. Although targeted at a return to economic and financial stability in the wake of the euro area crisis, the measures taken by the respective authorities show a distinct similarity to the application of financial repression tools known from the past.
The advantages of generating fiscal space through non-standard means must be weighed against the economic costs of treasuries pressing domestic investors to adopt a home bias in their sovereign portfolios and thus promoting a fragmented EMU capital market. In addition, the strong demand for public debt generated by a combination of moral suasion, financial legislation and supervisory pressure could crowd out private credit and become a danger to financial stability in new episodes of fiscal stress (ESRB, 2015). Furthermore, the preferential regulatory treatment of sovereign debt in Europe and the ECB’s non-standard monetary interventions have likely weakened market-based incentives for governments to pursue sound public finances and to progress with structural reforms (cf. Hoogduin and Wierts, 2012). Moreover, official sector support from partner countries and public debt resolution at the expense of private creditors established large income and wealth transfers to crisis-hit countries without a corresponding strengthening of market discipline to counter excessive sovereign borrowing. The attendant longer-term risks for the functioning of EMU need to be addressed by giving a stronger role to market forces to ensure that euro area countries remain fully responsible and accountable for the sustainability of their public debt.
Figure 3: Nominal GDP growth and implicit government interest rate, 1995-2018
(percent per annum)
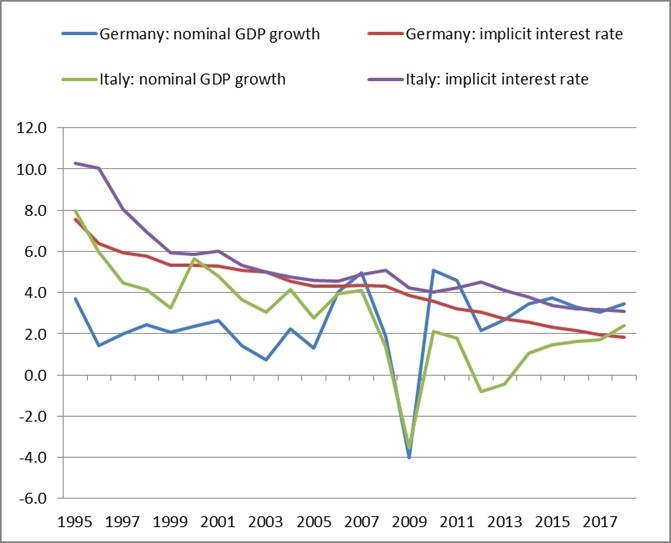
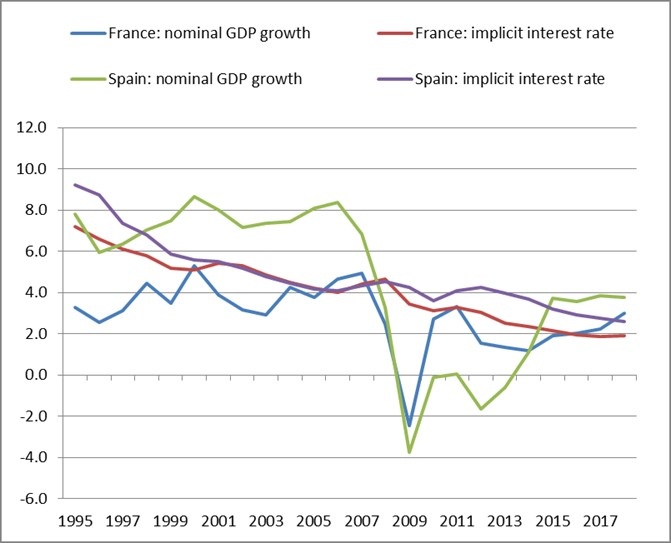
Source: ECB, Eurostat and European Commission economic forecast of spring 2017.
Alesina, A. (1988), The end of large public debts, in F. Giavazzi and L. Spaventa (eds.), High public debt: the Italian experience, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, pp. 78-79.
Aloy, M., Dufre not, G., and Pe guin-Feissolle, A. (2014), Is financial repression a solution to reduce fiscal vulnerability? The example of France since the end of World War II, Applied Economics, Vol. 46, No 6, pp. 629-637.
Bastasin, C. (2015), Saving Europe: Anatomy of a Dream, extended 2nd edition, Brookings Institution, Washington DC.
BCBS (Basel Committee on Banking Supervision) (2017), The regulatory treatment of sovereign exposures – discussion paper, Bank for International Settlements, Basel.
Bradley, M., and Gulati, M. (2014), Collective Action Clauses for the Eurozone, Review of Finance, Vol. 18, Issue 6, pp. 2045-2102.
Chari, V.V., Dovis, A., and Kehoe, P.J. (2016), On the Optimality of Financial Repression, Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis, Research Department Staff Report, No 1000, October.
Corsetti, G., Erce, A., and Uy, T. (2017), Official Sector Lending Strategies During the Euro Area Crisis, Centre for Economic Policy Research, Discussion Paper, No 12228, August, revised September, London, UK.
De Grauwe, P. (2012), The governance of a fragile eurozone, Australian Economic Review, Vol. 45, Issue 3, September, pp. 255-268.
De Marco, F., and Macchiavelli, M. (2016), The Political Origin of Home Bias: The Case of Europe, Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, Finance and Economics Discussion Series, No 60, New York.
Eijffinger, S.C.W., and Mujagic, E. (2012), The Age of Financial Repression, Column on Project Syndicate, 21 November.
Eijffinger, S.C.W., Kobielarz, M.L., and Uras, B.R. (2018), Sovereign default, exit and contagion in a monetary union, Journal of International Economics, Vol. 113, July, pp. 1-19.
ESM (European Stability Mechanism) (2017), 2016 Annual Report, Luxembourg.
ESRB (European Systemic Risk Board) (2015), Report on the regulatory treatment of sovereign exposures, Frankfurt am Main.
Große Steffen, C., and Schumacher, J. (2014), Debt Restructuring in the Euro Area: How Can Sovereign Debt Be Restructured more Effectively?, DIW Economic Bulletin, Vol. 4, No 10, 17 November, pp.19-27.
Holler, J. (2013), Funding Strategies of Sovereign Debt Management: A Risk Focus, Oesterreichische Nationalbank, Monetary Policy & The Economy, Q2/13, pp. 51-74.
Hoogduin, L., O ztu rk, B., and Wierts, P. (2011), Public debt managers’ behaviour: interactions with macro policies, Revue économique, Vol. 62, No 6, pp. 1105-1122.
Hoogduin, L., and Wierts, P. (2012), Thoughts on policies and the policy framework after a financial crisis, in Bank for International Settlements (ed.), Threat of fiscal dominance?, BIS Paper, No 65, May, pp. 83-90.
McKinnon, R.I. (1973), Money and capital in economic development, Brookings Institution, Washington DC.
Ongena, S., Popov, A., and Van Horen, N. (2016), The invisible hand of the government: “Moral suasion” during the European sovereign debt crisis, European Central Bank, Working Paper, No 1937, July.
Reinhart, C.M., Reinhart, V.R., and Rogoff, K.S. (2015), Dealing with debt, Journal of International Economics, Vol. 96, Supplement 1, July, pp. S43-S55.
Reinhart, C.M., and Sbrancia, M.B. (2015), The liquidation of government debt, Economic Policy, Vol. 30, Issue 82, April, pp. 291-333.
Shaw, E.S. (1973), Financial deepening and economic development, Oxford University Press, New York.
van Riet, A. (2018), Financial Repression and High Public Debt in Europe, CentER Dissertation Series, No 551, Tilburg University, Netherlands.
Véron, N. (2012), Banking union or financial repression? Europe has yet to choose, Column on VoxEU, 26 April.
Véron, N. (2014), Defining Europe’s Capital Markets Union, Bruegel Policy Contribution, Issue 12, November.
Zettelmeyer, J., Trebesch, C., and Gulati, M. (2013), The Greek debt restructuring: an autopsy, Economic Policy, Vol. 28, Issue 75, July, pp. 513-563.
This policy note draws on van Riet (2018). The views expressed are those of the author and should not be reported as representing the views of the European Central Bank. Comments from Sylvester Eijffinger, Lex Hoogduin and two referees are gratefully acknowledged. © Ad van Riet, May 2018.
The term ‘financial repression’ can be traced back to McKinnon (1973) and Shaw (1973), who studied how developing countries with incomplete capital markets repressed their financial system. But financial repression also has a long history in advanced economies with more developed capital markets, especially to ease the government budget constraint during and after episodes of war and crisis, when it took the form of administrative controls on bank rates and capital flows, suppressed sovereign bond yields, directed credit, monetary financing, capital levies, etc. (Alesina, 1988; Aloy et al., 2014; Reinhart and Sbrancia, 2015).
Chari et al. (2016) show that a crisis-affected government faced with the need to issue a large amount of debt should use financial repression techniques, in particular by obliging local financial intermediaries to hold more public debt on their balance sheet until the crisis has passed and the extra debt has been run down.
Negotiations at the international level to remove or reduce the preferential regulatory treatment of sovereign exposure in banking law have not led to any consensus (see BCBS, 2017).
The euro area CACs require at least 66.67% (in value terms) of the holders to agree to a change in the payment terms of an individual outstanding sovereign bond (which compares with a typical minimum threshold of 75%). Moreover, an aggregation clause allows the debtor to apply the modification of the payment terms simultaneously to all outstanding sovereign bonds, provided that at least 75% of the holders across all bond series agree.